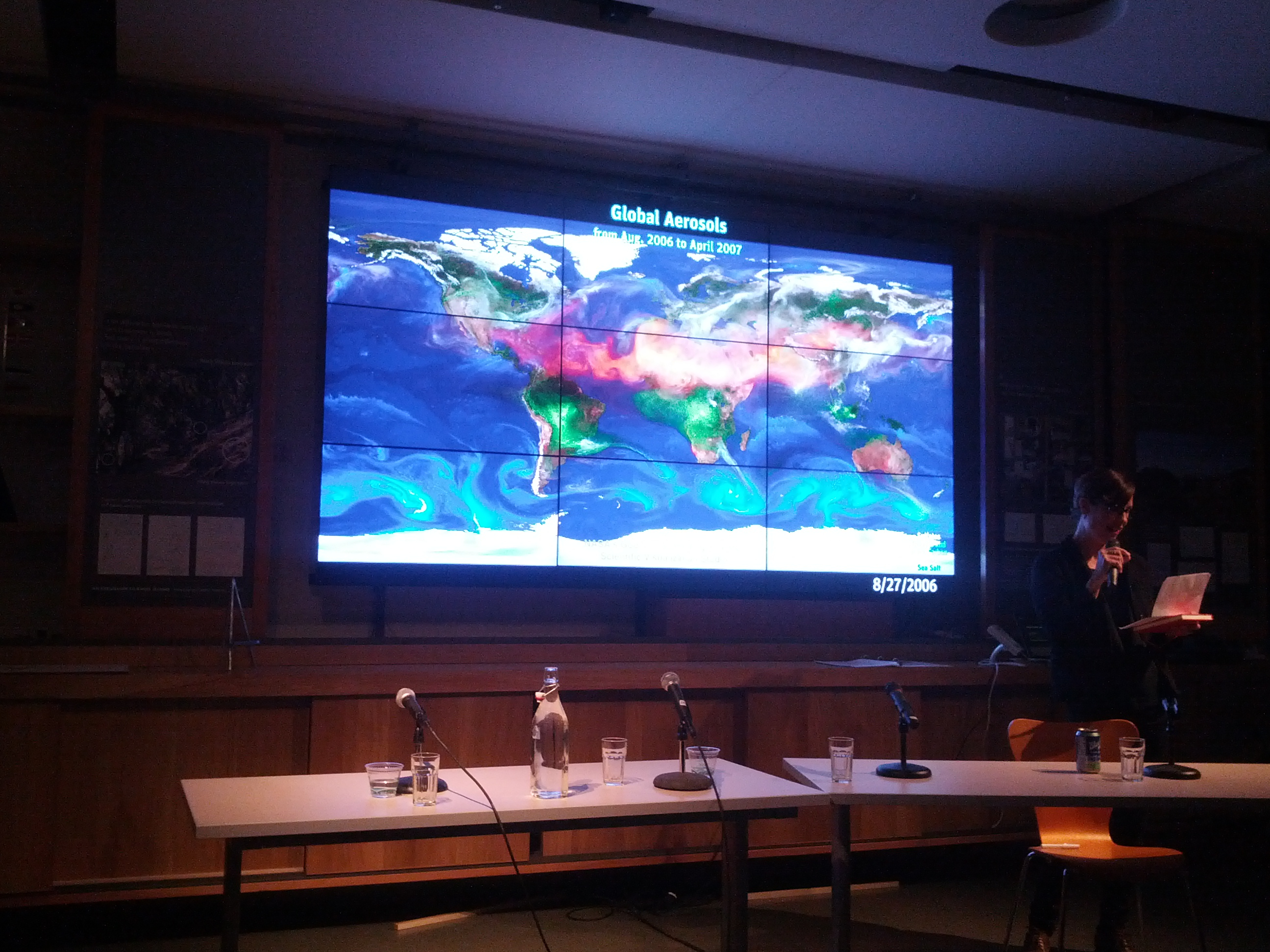
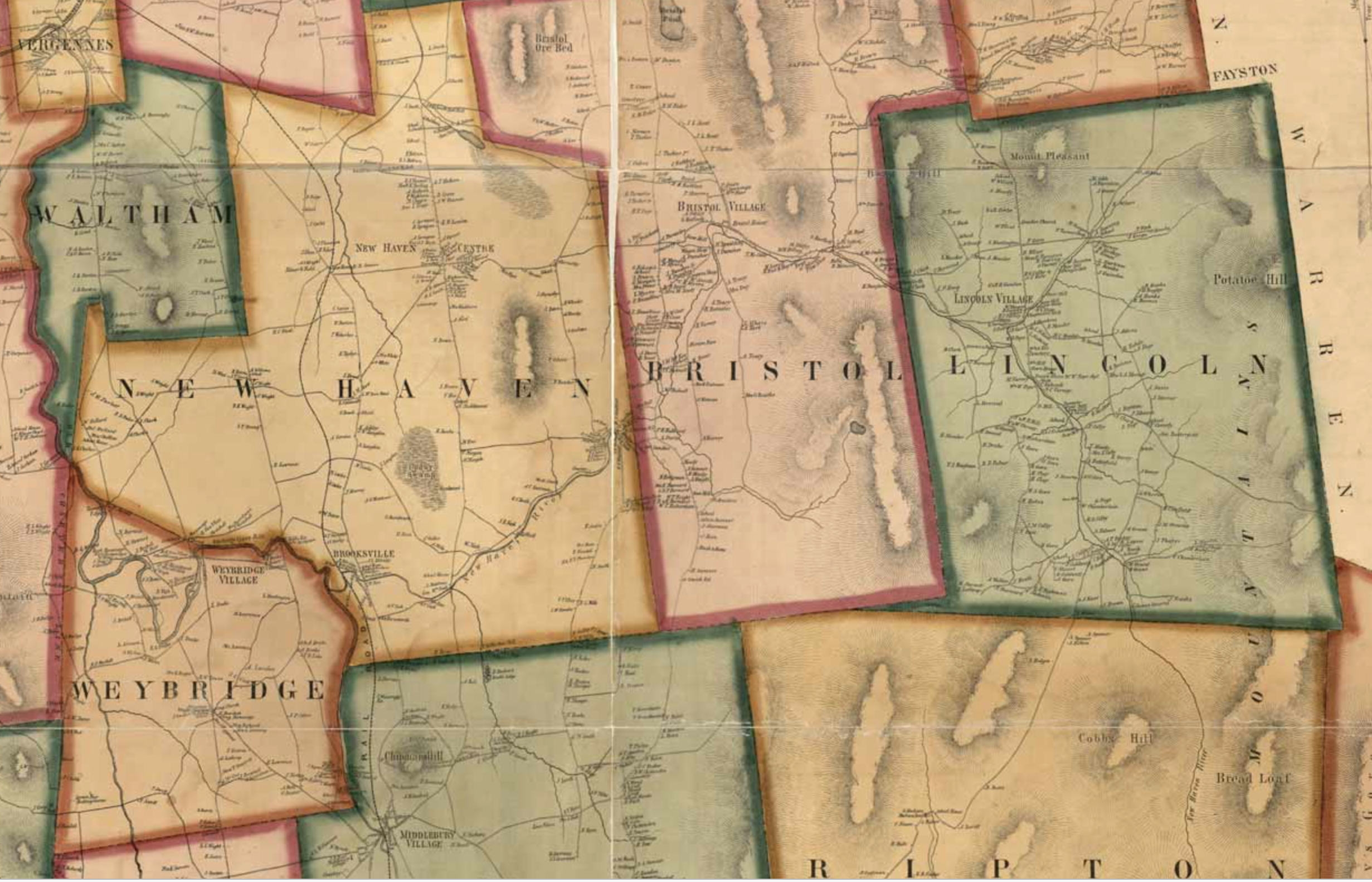
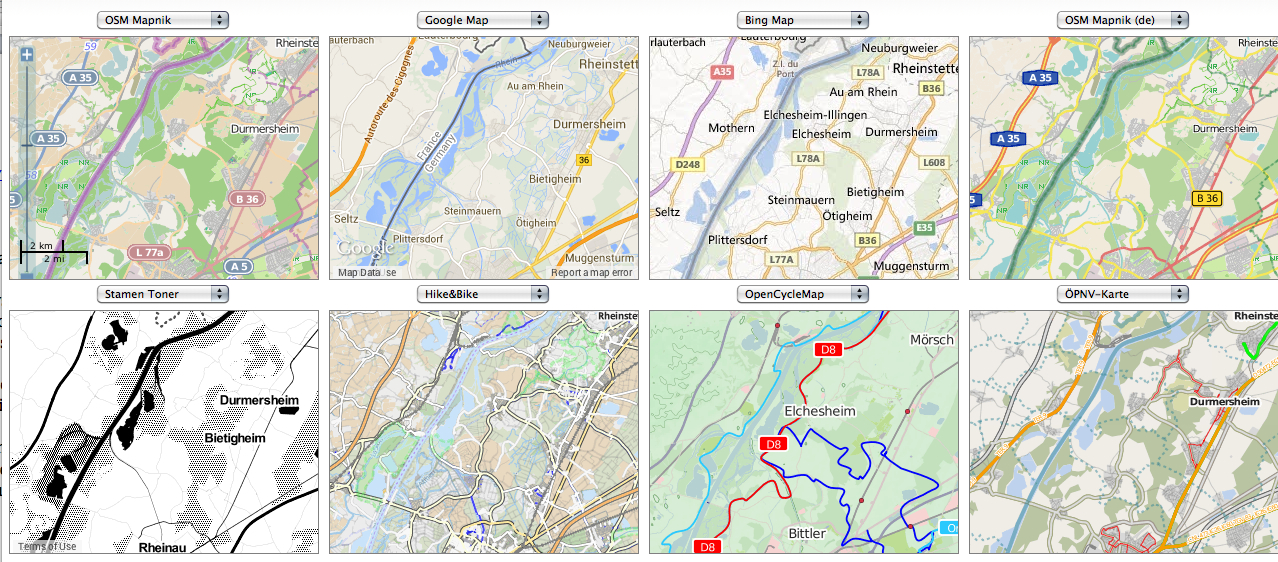
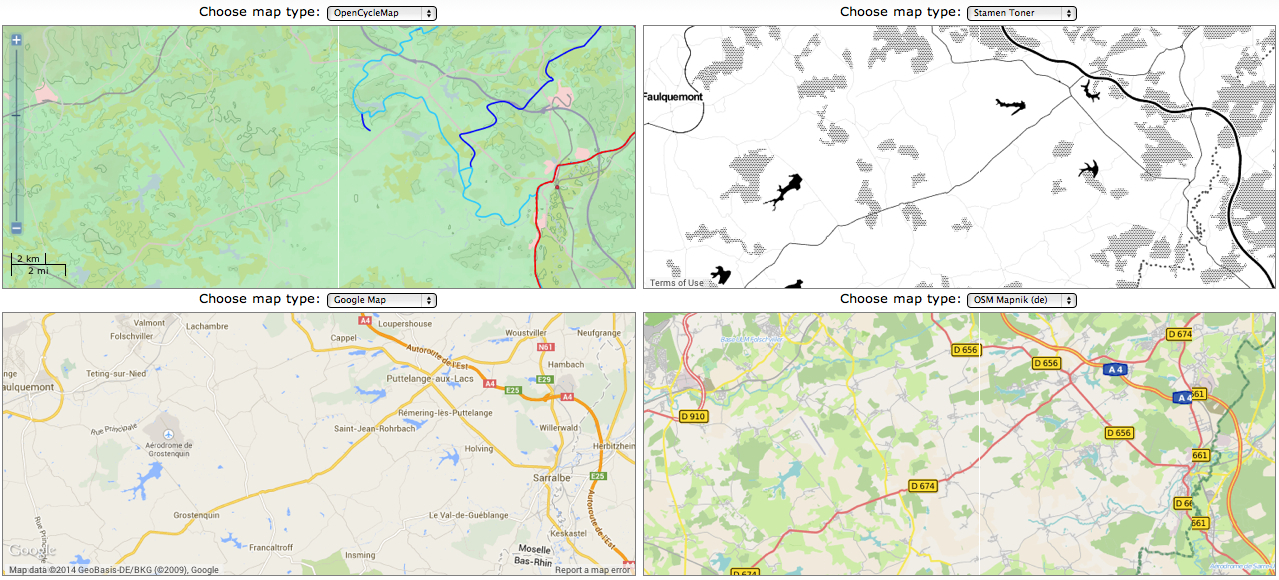
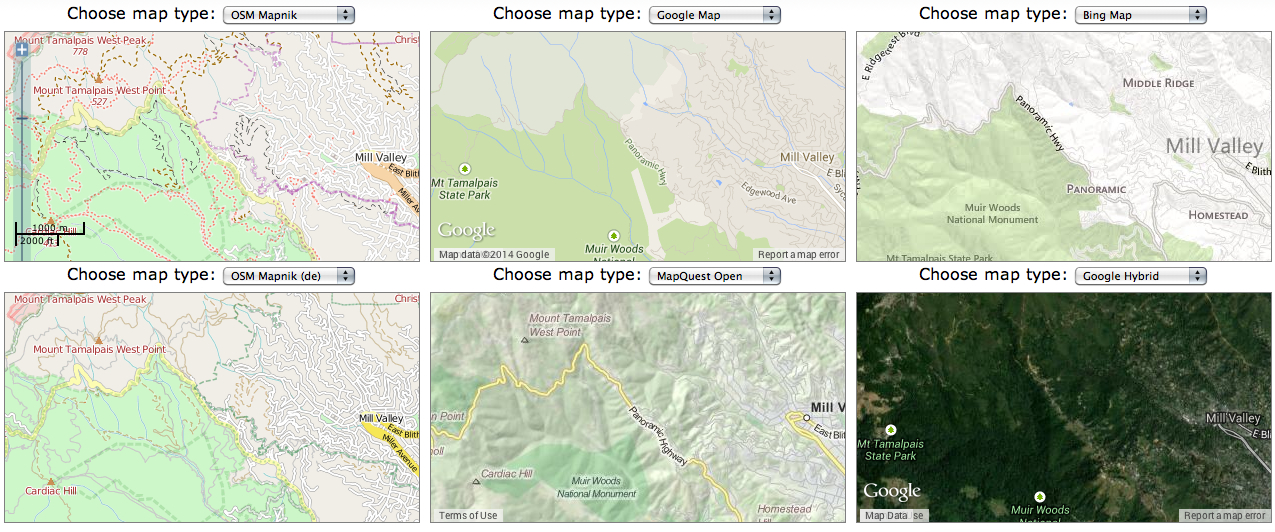
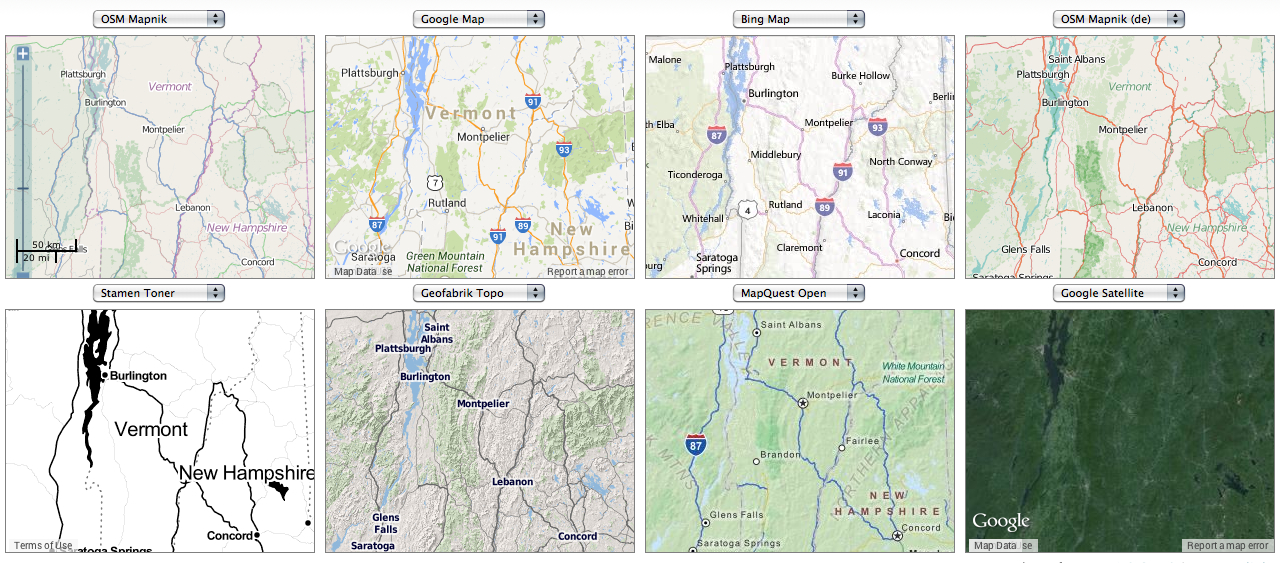
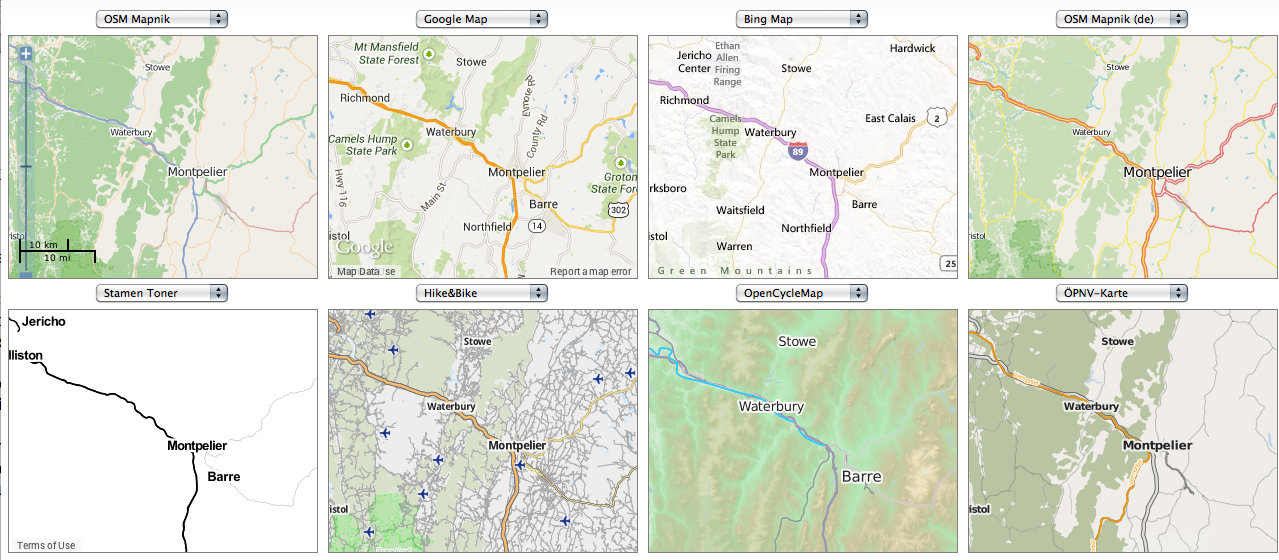
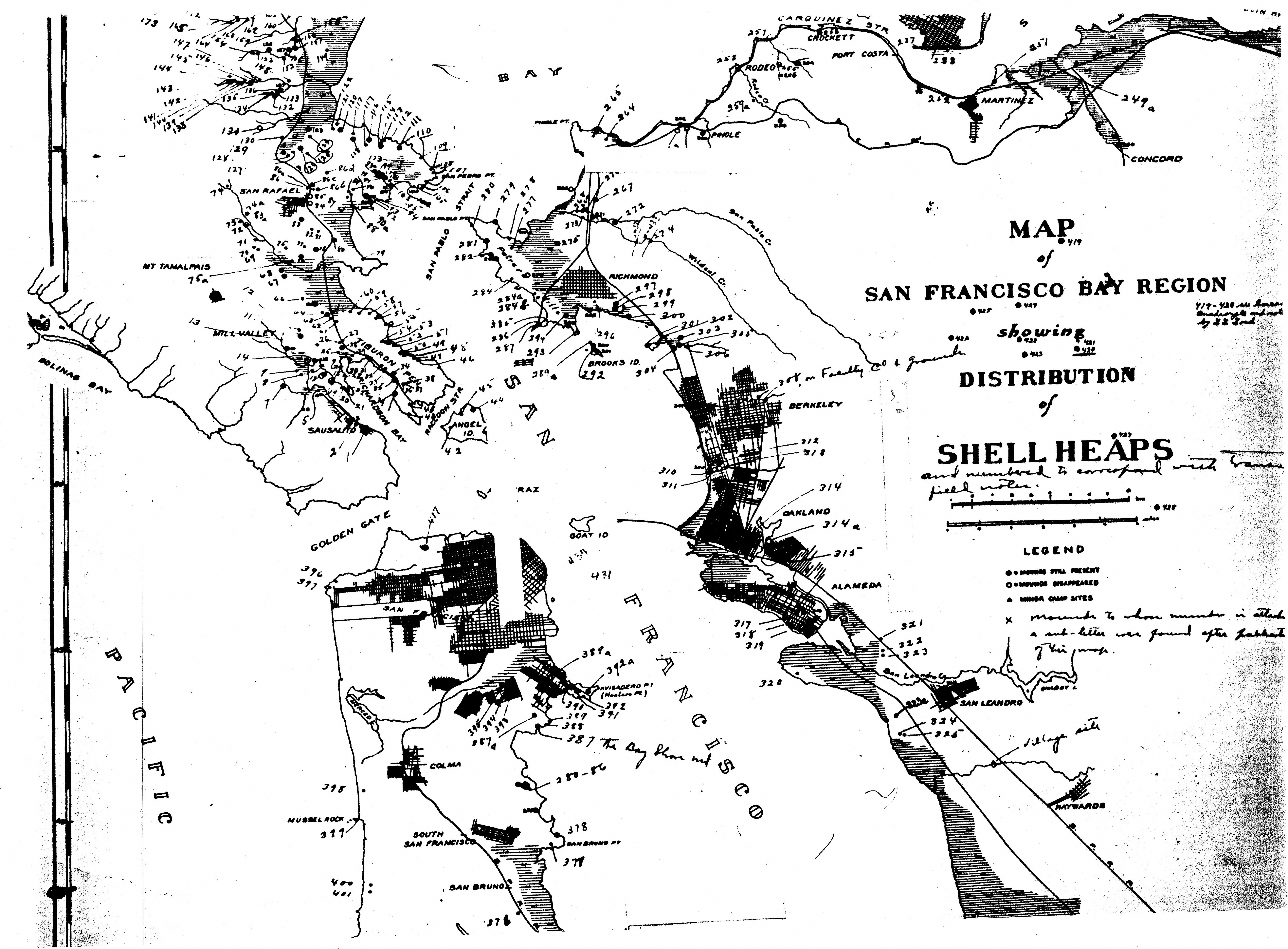
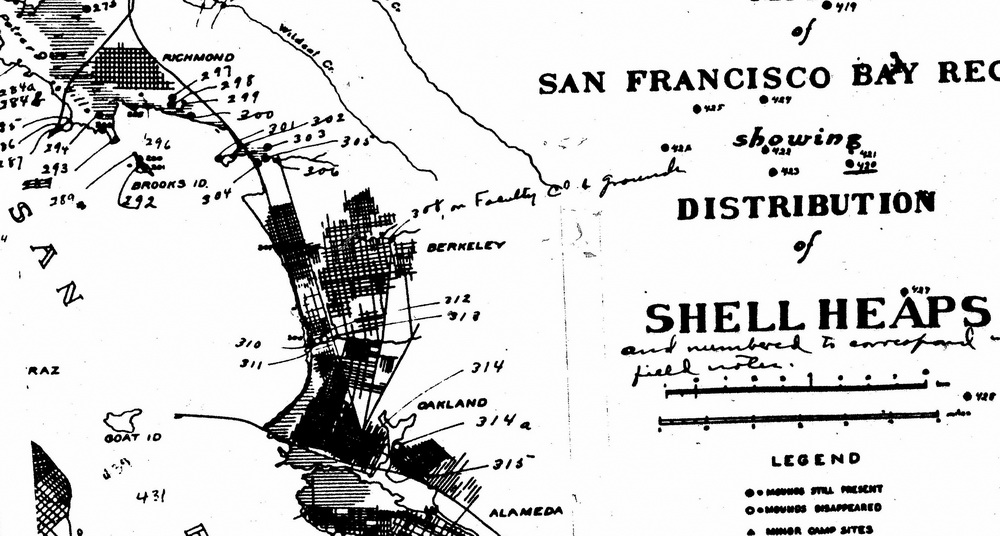
What’s the significance of names on a map? Do they register roads that belong to the territory or only reflect continued use? What sort of authority does a mapped road, byway, or highway retain in common law–and for how long must it be recognized as a road? The existence of place-names and routes on a map have become an increasingly contested way to preserve a sense of place, and the survival of the “sleeping roads” of Vermont, the “Class 4” roads that are not maintained by towns, even if some receive some limited maintenance, suggest a historical network of the past, still partly visible and indeed rarely used, but providing a vanishing network of the past inhabitation of rural space and its organization before the introduction of the interstate system.
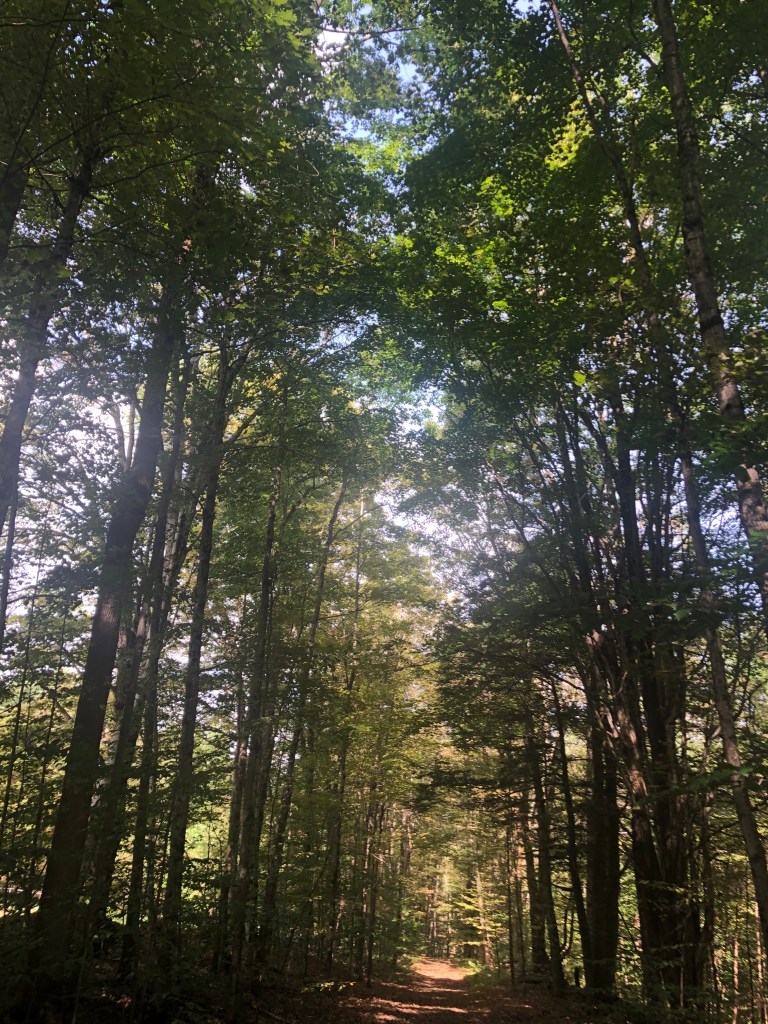
“If you walk down that road,” a Vermont farmer gestured at the end of Lavender Road in Central Vermont, “it’ll be like you’re walking into the past.” Meaning that the flat stone walls bordering the path, now overgrown with ferns, fallen logs, exposed granite, and an abundance of mushrooms and twigs, not to mention suspicious looking poison ivy, was an earlier system of land management and division, as well as an earlier route of access among the private property that divided Central Vermont hills, Long before I-89 ploughed through the countryside of central Vermont as a central artery of automotive traffic, cut through dark bedrock of metamorphic Cambrian and Ordovician eras, seizing thousands of acres across the state and displacing houses and farms, the roads we now see as arteries that cut through old forests and Silurian and Devonian metasedimentary rocks displaced the roads that once defined travel, reducing once luscious habitats of oak forests to the veils of Potemkin forests. Those illusory strips of six to ten trees deep to create the illusion of forest for tourists and motorists on the highways that cut across New England, vestiges of an earlier arboreal ecosystems living only in the minds of motorists on paved roads from which they rarely deviate or depart.
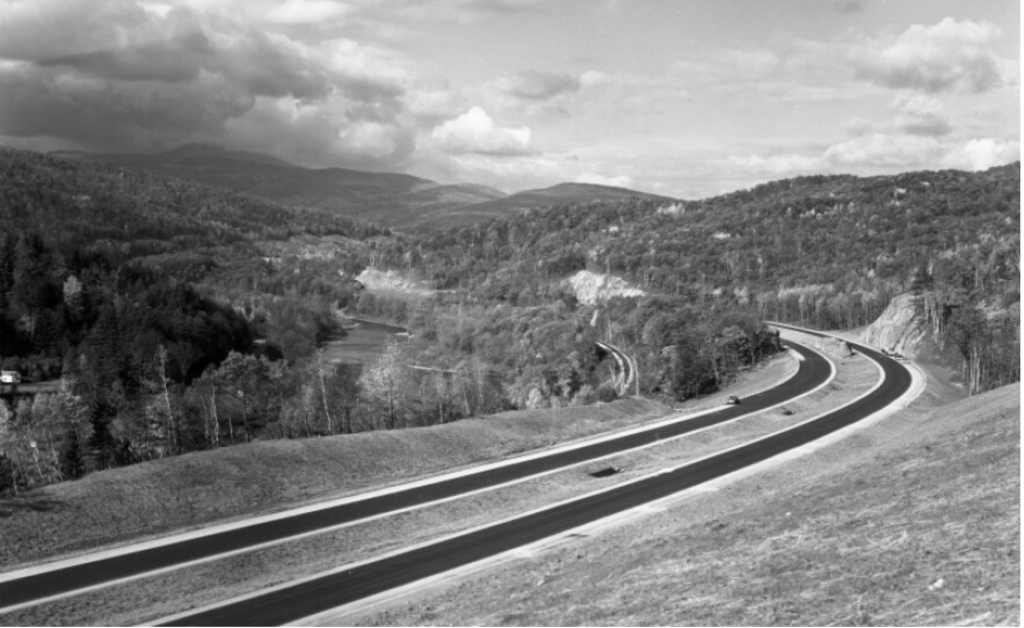

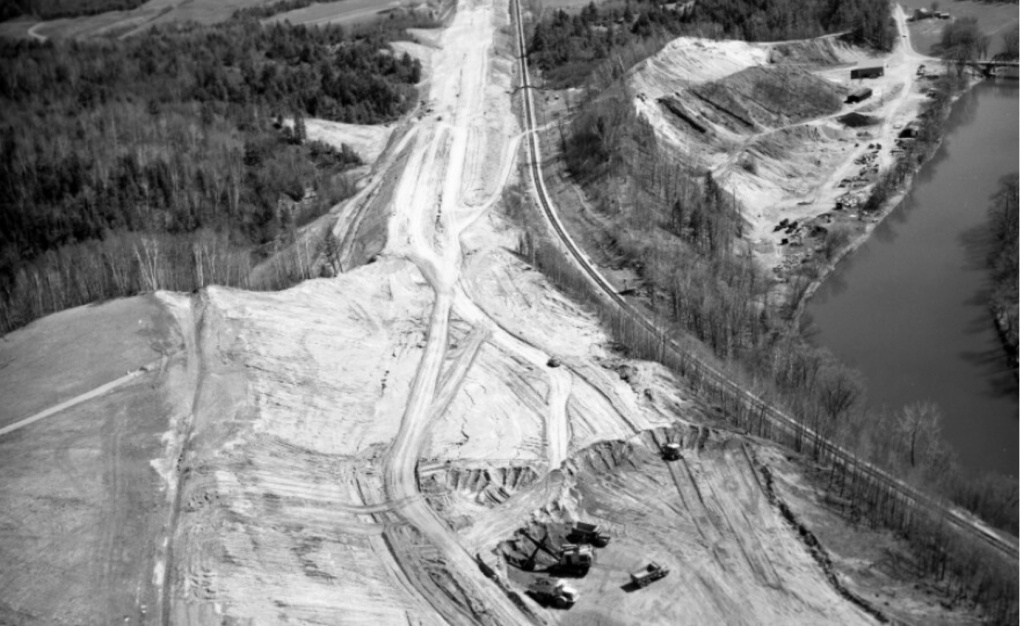
Newly Paved Interstate Curves through the Waterbury/Middlesex region, circa 1960/Vermont Historical Society
The very same roads that are no allowed to afford prospects of the fall foliage for which the same landscape is so well known were, of course, creations of an earlier area of land-movements and massive landscape shifts. What roads lie beneath them? How can they be seen or even mapped?

Interstate 89
The survival of so many earlier “sleeping roads” are increasingly threatened in an age of the road. The increased division of the long predominantly rural state on property lines, driven by a market of construction threatens to obscure local knowledge and a long-valued sense of place that the cutting of highways had long altered. If the preservation of dirt roads without much gravel in Vermont towns was an early development, which contributed recently to the real fears of erosion with flash floods and inundations, the drainage problems of the considerable number of municipal roads in the state have remained largely unpaved–about 75% in 2018, of municipal roads that comprise some 70% of total road miles–the problem of best drainage practices are an inheritance of the longstanding protection of the states rural character in its towns. But the landscape of the interstates brought a deep local resistance to the remapping of interstates and federal roadways that Vermont towns were quick to protect their local character in keeping with a longstanding agrarian economy, rooted in pasture and the production of cows’ milk.
Yet the increased presence of paved miles, even despite the increased danger that the state faces from stormwater damage and erosion in cases of increased stormwater and river inundations, has threatened the value of local roadways. The rapidity with which many roads were re-graveled, and provided with new culverts, ditches, and drainage systems after they washed out in the massive rains of the summer of 2023 led to a sense global warming as the latest threat conspiring to wash out the old lattice of historic roads in the state, and a quick and rapid defense of the local roads that were so much of the tourist industry depends. The deep sense of injustice in the prospect of loosing the legal status of “ancient” and long-pathways preserved in records of in local townships face possible obliteration in the legal memory as such unpaved roads–often more tacitly known than still used for commerce–are going to be reclassified. Indeed, as the state’s legislature has decided to reclassify common law roads to homogenize property records across the state, the outburst of local mapping seems not an act of antiquarian obscurantism, but a defense of local knowledge in an age of globalism and satellite mapping, where few of the older roads might appear from the sort of satellite-based mapping systems on which we increasingly depend. While many of the “class 4” roads might be sought out by mountain bikers, eager for off-road experiences, or back roads where they can snake around mountain farms, but only maintained if deemed necessary for the public good. Yet the rediscovery of these “ancient roads” that are still able to be found on some edges of historic farmlands open up prospects of the topography of the past, evident in the gaps between tree tops and the old stone walls of the edges of the pathways, rather than their navigability or use.
The plan for a massive reclassification of “ancient” highways on the books but actually dormant in much of the state of Vermont may be a pro-development land grab, but suggests that the struggle for designating once common lands as private property (and resistance to it) are waged on maps. The recent promise to reclassify registered but unnamed byways in the state–a mass of roads which were at one time used or previously surveyed as common-law byways, but have since fallen out of use to different degrees–has unintentionally generated a set of local storms about public memory. In a state where many current town roads remain unpaved, and many more have faded into the largely forested landscape, their traces still in evidence in the midst of a somewhat bucolic space of passage, tree growth impeded by the stones and often muddy road between old flat stone walls that had once been built to separate famers’ bow long overgrown fields.
The drive to reclassify the diversity of unpaved roads and common law byways once preserved in local jurisdictions reveals the rise of property development for whom the retention of old systems of spatial classification obfuscates the exchange of private lands. And if the preservation of old farmlands in Vermont provided a rare historical perspective of longue durée for early twentieth century historians as George Perkins Marsh, who rote long before the rise of environmental history or of the Annales school focussed on land management practices as a lens to observe long-term changes in social history. And in a fascinating illustration of how local collective mapping practices provide a unique point of resistance to mapping software systems that are primarily oriented to paved space, rather than the commons, or, as it is now known, the closely connected right to wander.
The Vermonter developed a broad history of the dialectic relations of what we call the Anthropocene between “man” and “nature” avant la lettre. He dis so out of a deeply American vantage point on world history, as he contemplated the “destruction wrought” on his native state’s local landscape in 1864, about twenty years after Henry David Thoreau lamented the presence of the intrusion of railway lines in the idyllic space of Walden Pond. He offered a global perspective that took its spin from his deep impression by the effects of the retreating and shifting landscape of Vermont, where he had been born in a farmhouse, the vantage point from which Marsh defined his perspectives on human destruction of the global landscape. After travels in Italy and study of the deforestation Mediterranean basin, he bemoaned that the case of Vermont’s loss of native trees as a similar global historical shift of consequence; in the introduction of his massively learned work, Marsh affirmed that “The earth is fast becoming an unfit home for its noblest inhabitant, and another era of equal human crime and human improvidence . . . would reduce it to such a condition of impoverished productiveness, of shattered surface, of climatic excess, as to threaten the depravation, barbarism, and perhaps even extinction of the species.” In his metahistorical masterwork, Man and Nature, Marsh contemplated the “wide a circle of disturbance we produce in the harmonies of nature when we throw the smallest pebble into the ocean of organic life” and watch it send ripples across the surface of a body of water, offering one of the more prescient images of the cascading effects of anthropogenic change in the Anthropocene.
Vermont’s deforestation was so accelerated and traumatic in scope that–long before the expansion of its interstate that destroyed farms, homes, and an agrarian economy–the state offered an important perspective for articulating an early environmental vision of the planet’s dire state that in 1874 Marsh found it to carry “the force of revelation.” As immersion in the resettlement of dustbowl refugees prompted historical reflection of self-made environmentalist Clarence Glacken, about man’s relation to the habitable environment; his experience of resettling refugees forced from farms by a lack of rain prompted sustained reflection on the relation of “man to environment” that resulted in the synthetic surveys he taught in the 1950s, which culminated in Far From the Rhodian Shore, a compendium of classical to enlightenment thought that was in the course of being complemented by a second volume when it appeared in cloth in 1976. If Glacken viewed the interaction of humanity and the environment as a baseline for humanism, the devastating experience of deforestation provided for Marsh a baseline for the dangerous rewriting of relations to the natural world; the scale of the deforestation witnessed in Vermont as a circumscription of access to natural worlds provoked a terrifying resonance with the deforestation of the Mediterranean he witnessed, leading him to view environmental change as a altering one’s relation to the world, when the logging industry clearcut oak, birch, below 2,000 feet in a massive harvesting of wood, producing 375 million board feet of wood by 1889, and leading the treeless slopes of Mt. Tom near a town known as “Woodstock” to experience massive soil erosion with hard rains that it altered its shape in Marsh’s own line of sight. His own reflection on “man [as] a disturbing agent” able to turn natural harmony to discords wherever he arrives generalized the land-altering consequences of clearcutting without constraint as a force of history: and whereas metahistorical interpretations of Hayden White and others may smell of the libraries where men like Michelet, Burckhardt, Marx and Vico worked, we might well map the alteration of lived environments provided the optic by which Glacken and Marsh structured pessimistic historical dialectics of their own.

The massive rewriting of Vermont’s once rich arboreal landscape by the 1890s was so extensive to alter the economy of the land and man’s relation to it. The scope of devastation was not without resistance as the old map of a relation to landscape was preserved, in no small part by th donation of a Middlebury legislator who incarnated local ideals of environmental stewardship by decrying devastation of “timber butchers”: as soil erosion was devastating local tourism, legislators founded a Forestry Commission, similar to the Board of Agriculture, leading Middlebury legislator Joseph Battell to act preemptively to purchase and donate a thousand acres of forested land comprising Camel’s Hump, Bread Loaf Mountain, and other peaks of the Green Mountains to the state so that they preserved their form–and later donated lands from Hancock to Fayston, to his alma mater, Middlebury College, a land grant that provided the nucleus of the broadleaf trees in the Green Mountains National Forest.
If the extraction of wood from the state’s lands reshaped the soil as the cutting of trees on many hills was accompanied by rise in quarrying to mine slate, granite, marble, and copper; often, smelting left wastelands behind in place of forested lands–leaving old growth trees to act as wayfinding signposts for a drivable road network created on cleared land, paved or graded to allow increased automotive traffic unsuited to dirt roads from 1908.
Did not the rebuilding of paved roads as Interstate 89 not encourage the growth of a fossil fuel economy in the 1960s as it cut across once forested terrain, forcing the vision of Marsh’s coherent landscape further into the receding past, as automotive space shifted the function, use, and scope of a local infrastructure of roads?
![The back of this 1964 photograph reads, "Unvailing [sic] of new gas signs on I-89." An exhibit at the Vermont History Museum features historic photos from before, during and after the construction of the state's interstate highway.](https://www.vpr.org/sites/vpr/files/styles/medium/public/201311/interstate-signs-2.jpg)
New Gasoline Station Signs placed along Interstate 89 (1964)/Vermont History Museum
The local resistance to such a reclassification of roads in the rural state, which has attracted its share of fierce defenders of the local rights of communities long granted precedents to federal or state law, make the proposed elimination of “Ancient Highways” from local law a matter of contention. The proposed reclassification of a multiplicity of roads poses a problem of having ceased to reflect the sort of use of landscape that developers want to encourage and private home-owners want to ensure. Given the shifting nature of land use in Vermont, where older houses are increasingly on the market, as smaller agricultural farms close and die out, a premium has developed for the clear definition of ownership without any liens or qualifications. Hence the increasing tensions between local municipalities in the state and any move by state government to abolish roads they long oversaw. In a sense, the increased interest in helping demand for fungible residential properties that can be sold without qualification have run up against the multiplicity of roads that have continued to remain on the books.
As the real estate market in Vermont seems poised to heat up in much of the state, and smaller towns face a demand for brisk sales and a large pool of properties arrive on the market, the state seeks to remove any obstacles to development or become notorious for arcane property laws, remapping the “ancient” roads of Vermont opts to treat them as ancient, and, far more than unpaved, not part of its future landscape. Yet the quilt of county regulations of roads that existed for most of the eighteenth century and was retained in most local maps before World War II reflected a local landscape of counties and townships rarely challenged before the arrival of interstate federal highways across the state during the 1970s, erasing the varied paths, trails, and common-law roads, long overseen by local city Selectboards and regarded as parts of the local landscape.
Continue reading