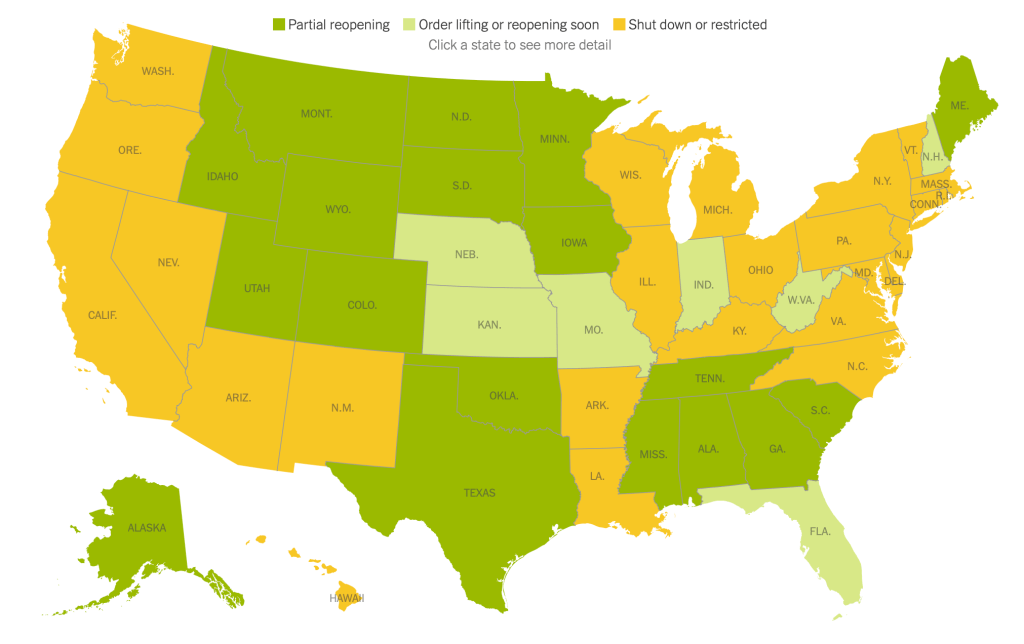
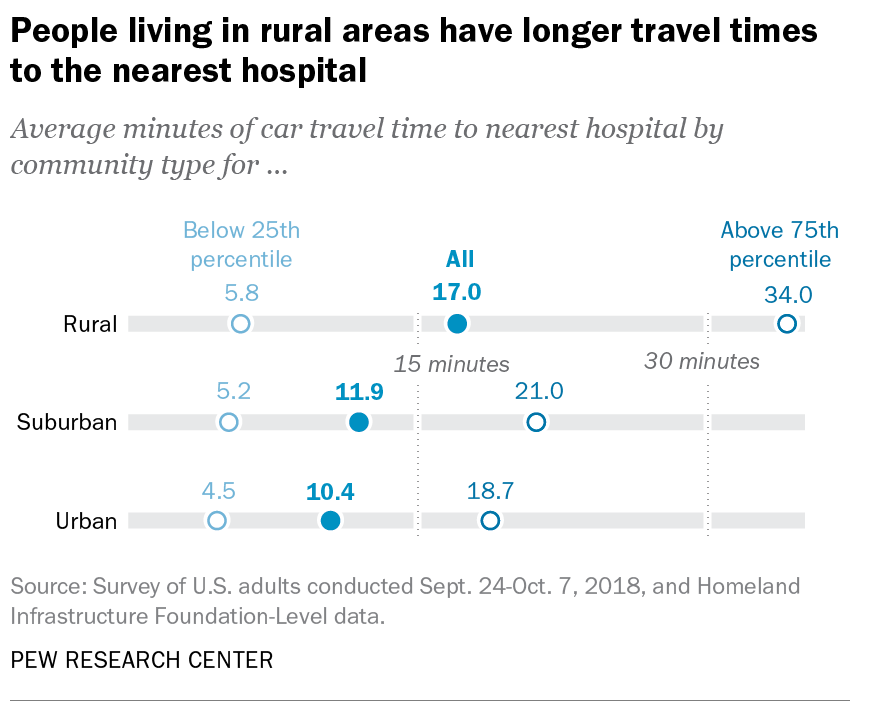Can we believe anything from the office of Governor Ron DeSantis? It was the height of irresponsibility, but one that should make Jack Dorsey breathe a sigh of relief that at last he is no longer responsible for Twitter: the Florida Secretary of State used bad data about the rates of COVID infection around the nation to trumpet the peninsula as a vacation land as a safe space in the pandemic, using an utter absence of ethics to promote disinformation about viral spread in the peninsula that almost echoed the denialism Governor DeSantis long promoted in bashing vaccines, masking, or market constraints as a way of combatting viral spread, even if his assertion ran against established ideas of contagious disease and viral transmission. Florida is facing numerous existential threats, from sea-level rise to saltwater flooding of coastal areas, but promotion of the state as a site of safety from the global pandemic was the height of duplicity.
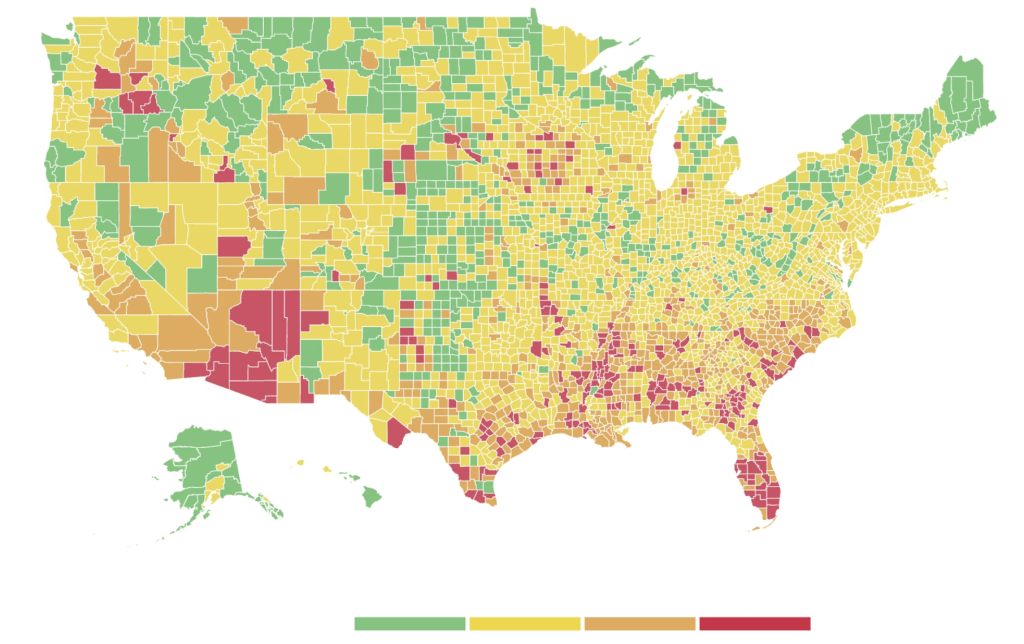
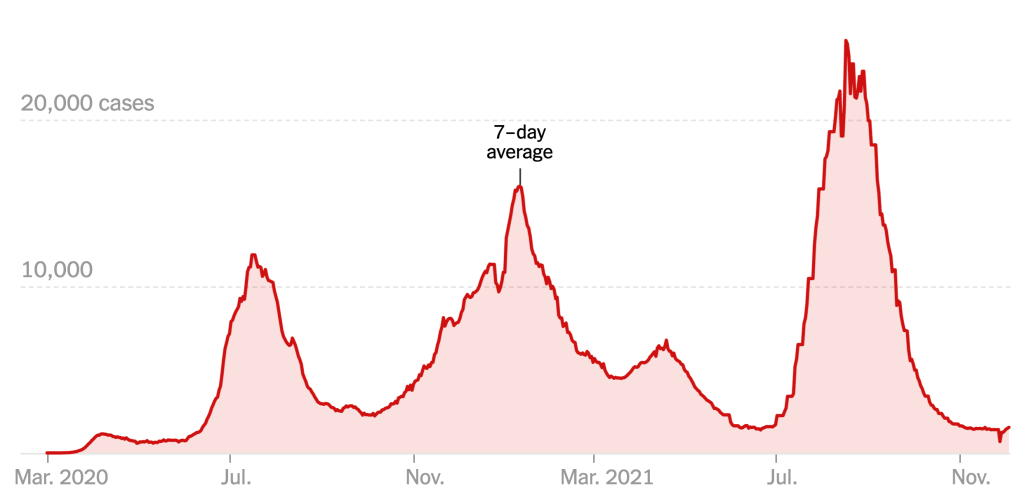
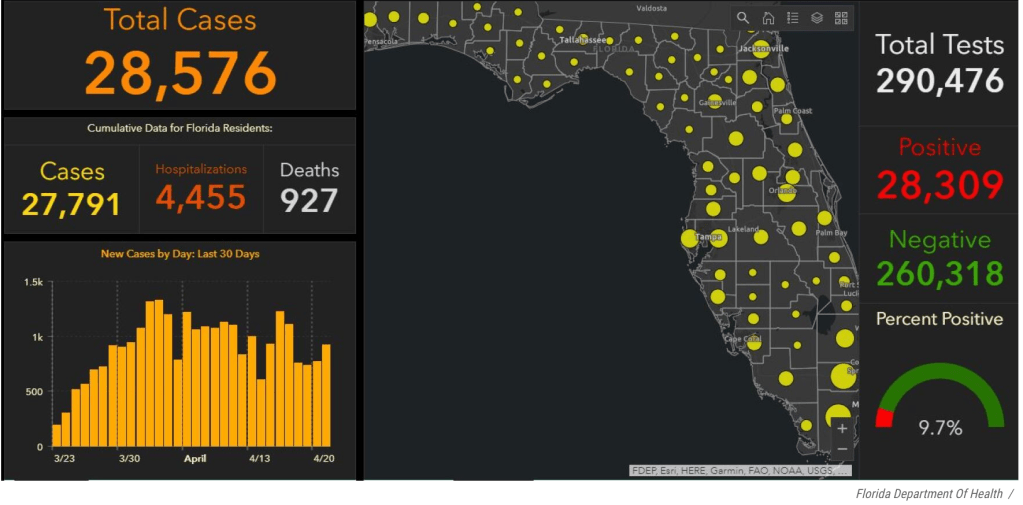
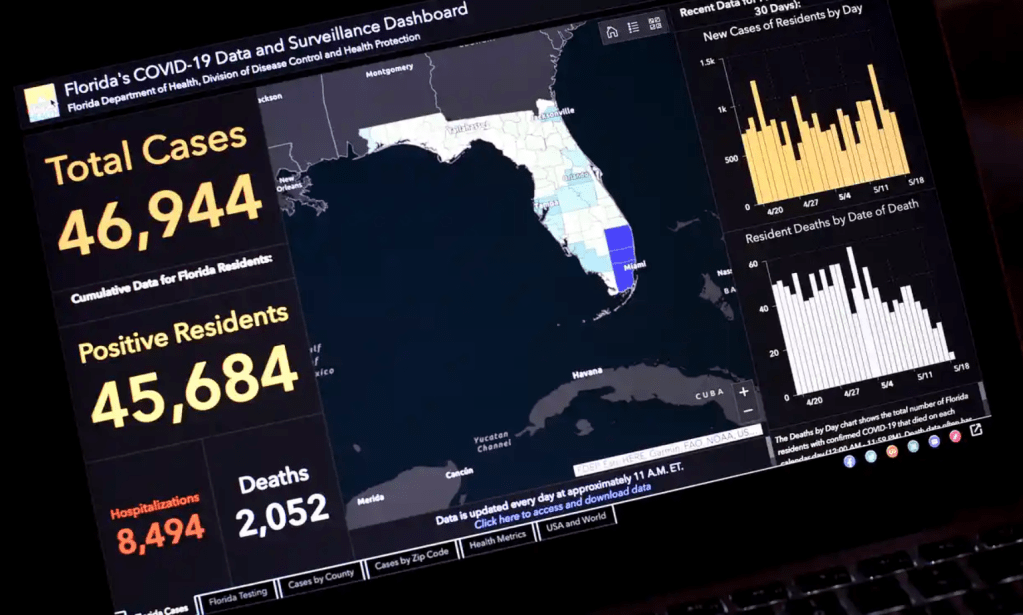
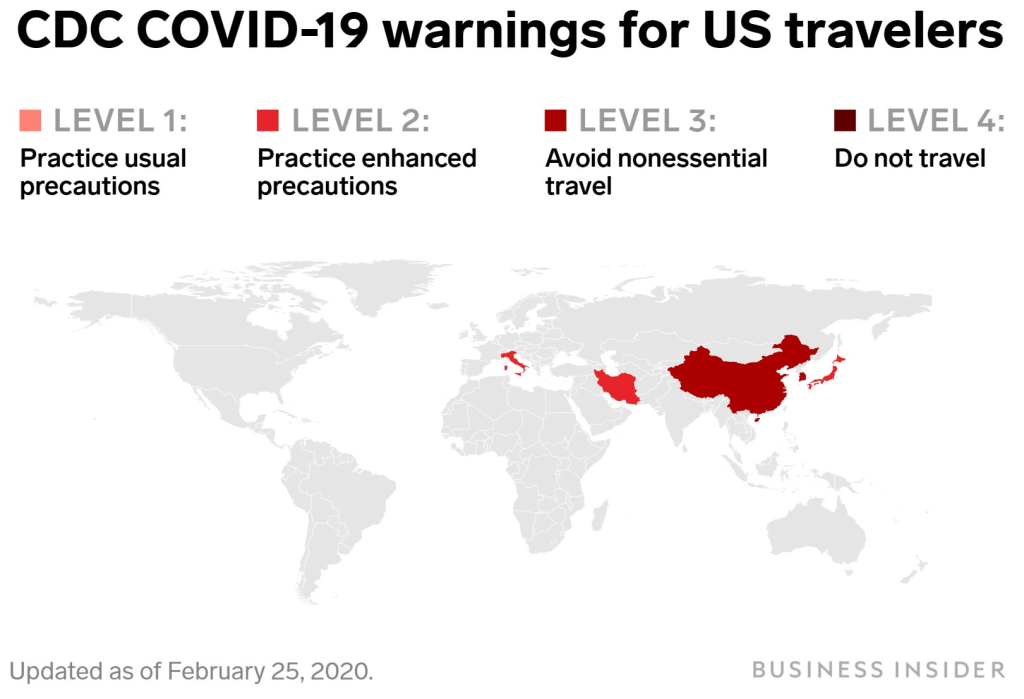
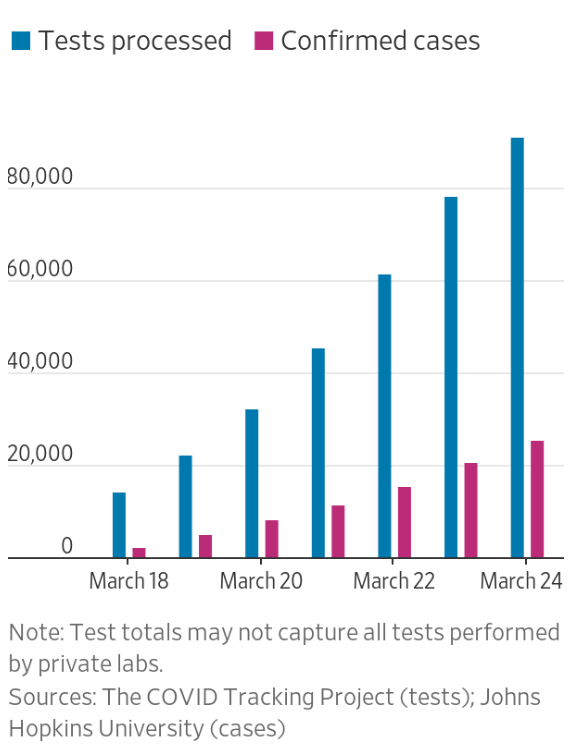
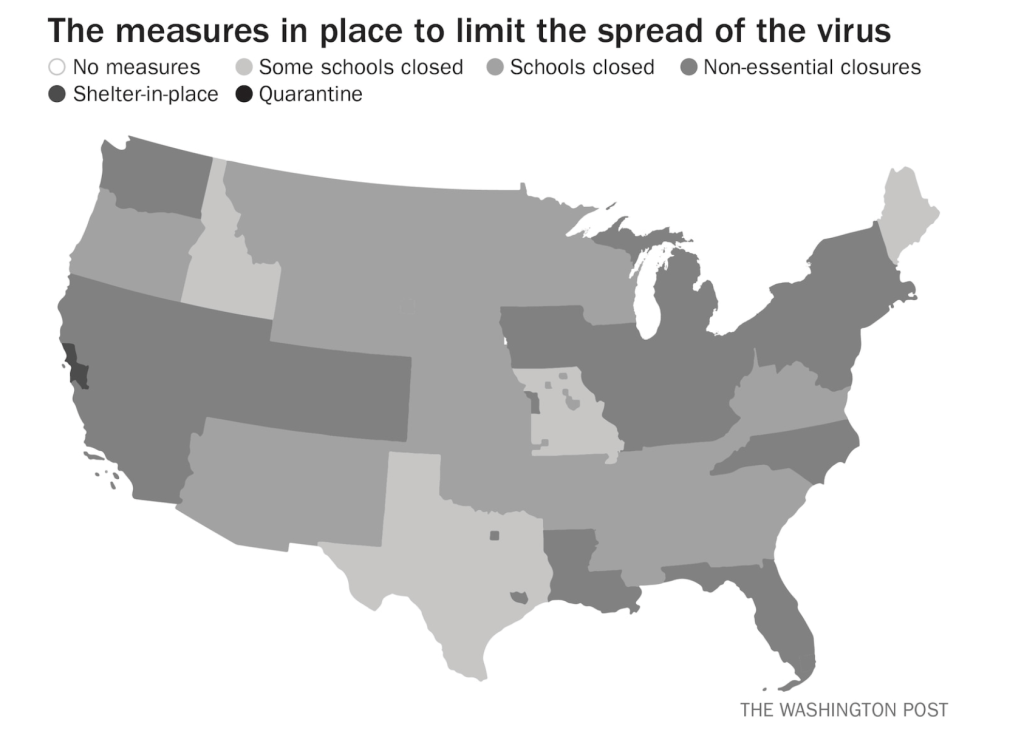
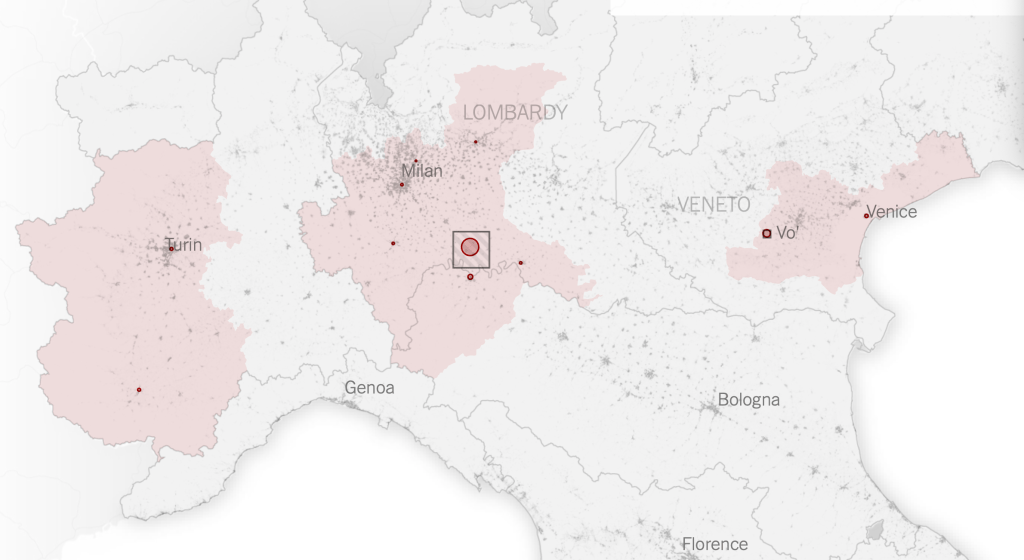
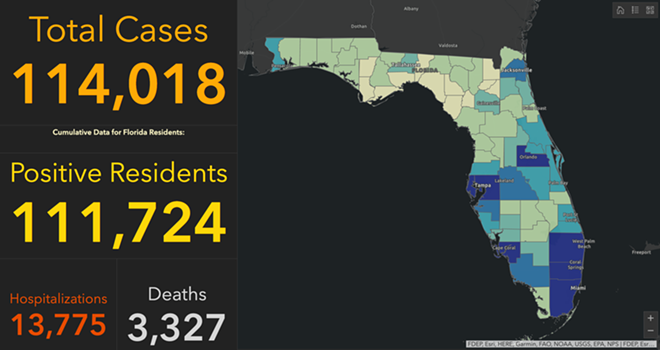
Exercising the prerogative DeSantis long claimed to guard the health practices of Florida, apart from the nation, his office and press secretary must have been thrilled at the latest pre-Thanksgiving COVID data vis that the issued by the CDC, that showed Florida as lying apart form the nation in a bucolic preserve of blue of low coronavirus transmission rates. The announcement by Florida’s Dept. of Public Health on June 8, 2020 of the first twelve deaths due to COVID-19 in the state of Florida 0, when just over 63,000 were testing positive in the state, led the DoH to promise to “provide more comprehensive data,” releasing daily reports on COVID-19 cases in Florida on the DOH COVID-19 dashboard is also providing updates once per day for every Florida county, “available here,” of new positive cases, that state residents and the nation watched rise. If folks had become habituated to dashboards as a way of accessing up-to-date data on viral transmission and public health, the tweeting out of a map that integrated outdated data on infections in Florida with shifting national picture as even as the arrival in the United States of an Omicron variant put a chill on national travel over the Thanksgiving weekend, but year-end travel was predicted to see a rise in air-travel that would approach pre-pandemic days.
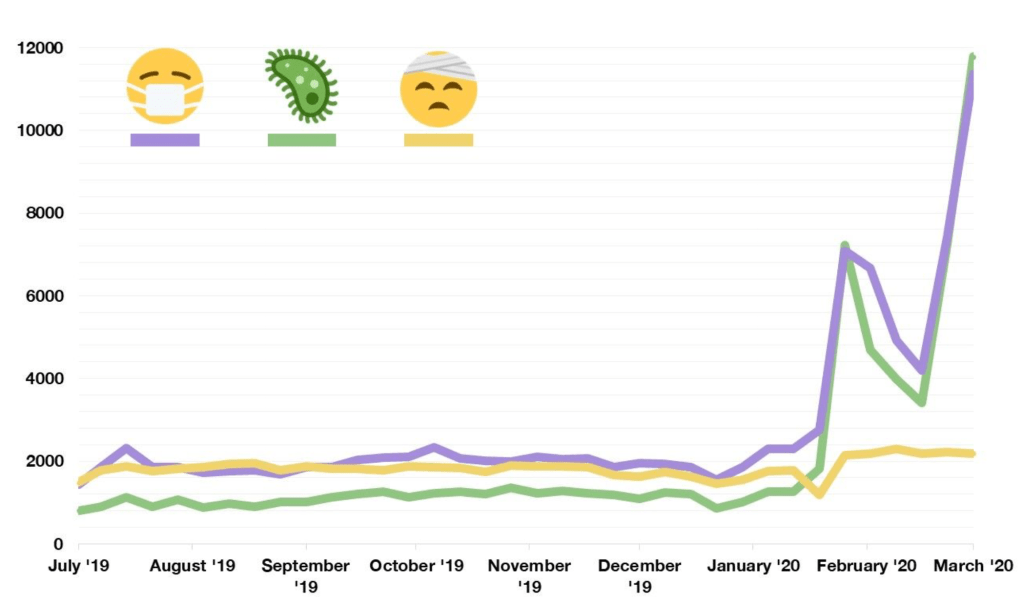
The Age of COVID has encouraged an amplification of graphic story-telling about the hot spots and safe spots of viral transmission or local virulence. And the infographic appearing to label Florida, the nation’s storied vacationland, as featuring far lower community transmission seemed ripe for a retweet. Caroline Pushaw, Florida Governor’s social media savvy press secretary, seems to have issued it as an invitation to the state’s winter beaches, as if Florida policies had, despite anti-vaccination campaigns and few masking mandates, gone beyond other states in reversing the high rates of COVID-19 mortality that once afflicted the state per public dashboards of years past.
Gov. DeSantis was a huge denier of the infectious nature of the virus, even resisting Trump’s own calls for Americans to stay at home when possible to contain virtual spread, arguing that imposing any “lockdown” and “shutting down the country” was an excessive response. DeSantis’ prominent place in Trump’s inner circle of response to the pandemic increased his profile in the COVID response, and inflated his own sense of national responsibility, as well as causing his pro-business policies to shift in March 2020 by closing Florida schools in the end.
The national map of community transmission rates attempted to bolster Gov. DeSantis’ national credibility. The arrival of the Omicron variant, boasting over three times as many mutations as the delta variant, became an opportunity to boost perceptions of Gov. DeSantis’ public health creds. Despite the Governor’s vaccine denialism and diminishment of public health risks–and utter lack of interest in vaccine equity–low rates of transmission offered a useful icon of peninsular identity to promote the governor on the national news, from FOX to OANN, as if to suggest that “as winter approaches,” Florida was doing something right–as if in an invitation to the nation to make travel plans to consider visiting the sunshine state.
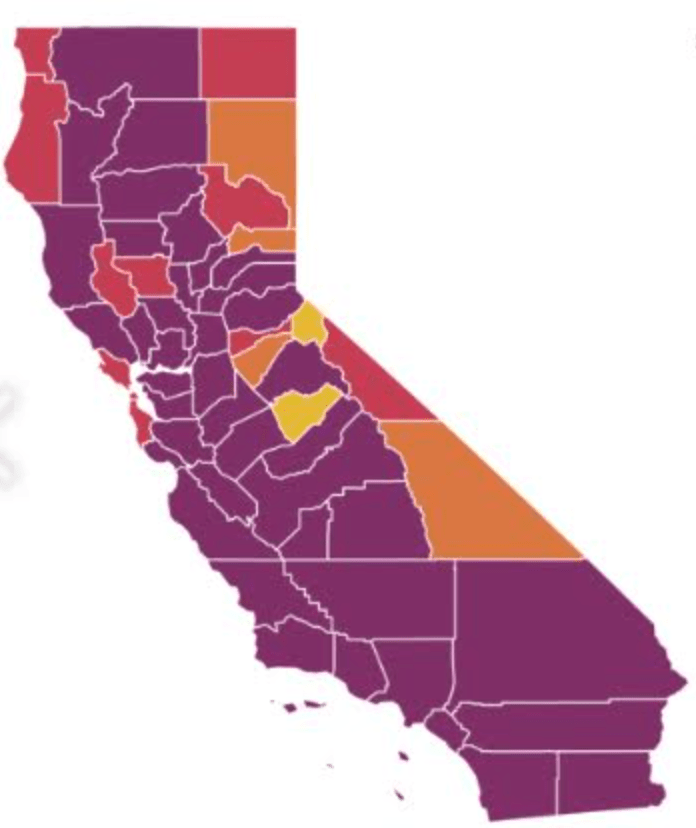
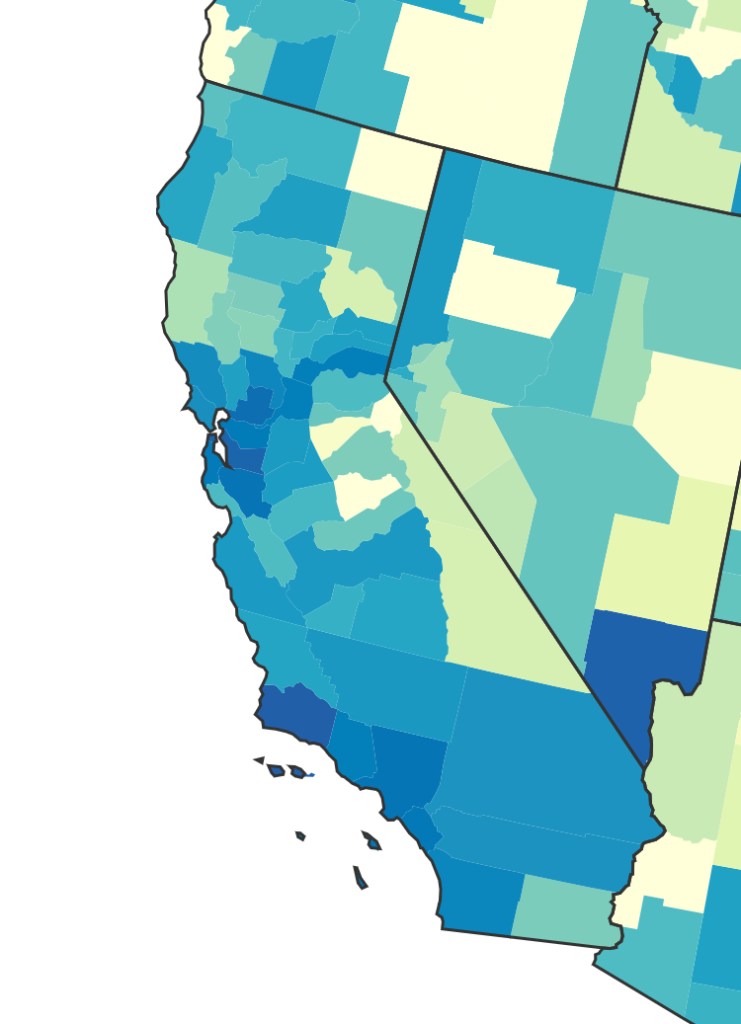
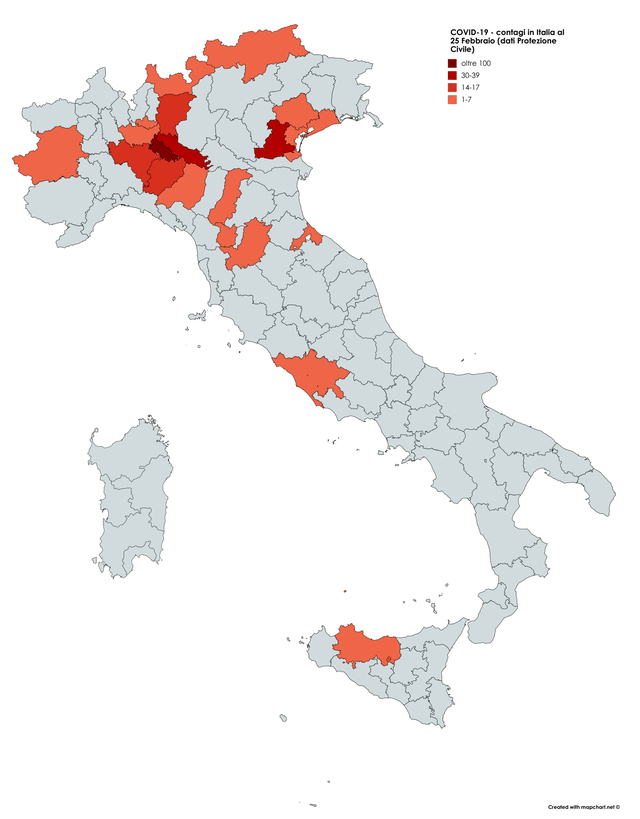
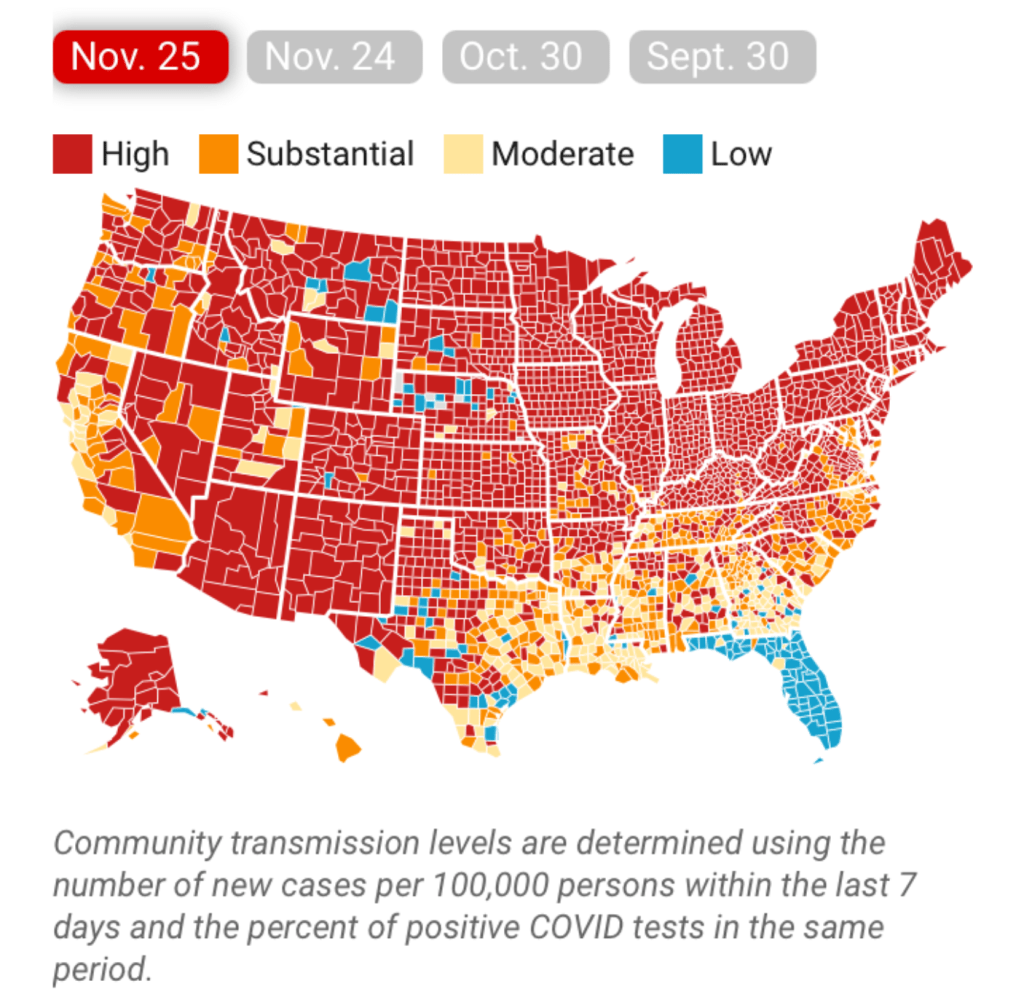
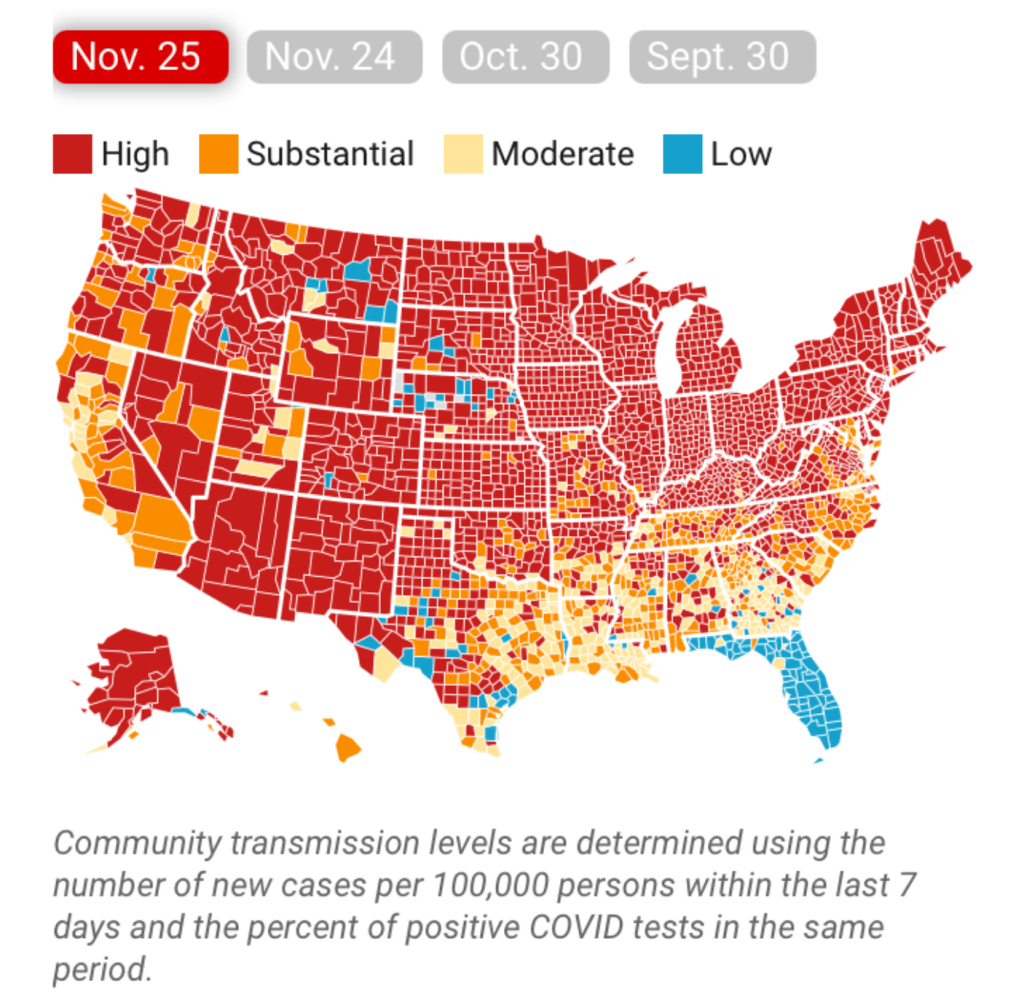
It must have been clear quite immediately to DeSantis’ press secretary, who tweeted it to her 22,000 Twitter followers as evidence of an ethically dubious ethical invitation to the Sunshine State for future travelers–per what seemed currently reported transmission levels. Strikingly, low levels of community transmission in most counties south of the Mason Dixon line would obviate the need for mask-wearing even in public after the arrival of new variants, although not the bulk of the nation, colored red for high levels of transmission that merited masking in the all counties colored red for high levels for which the CDC recommended masking in public to contain potentially very dangerous COVID-19 transmission in the form of new variants.
But the map “lacked” a legend and was in many ways cherry-picked–or based on cherry-picked data, as the statistics for infections in Florida were decisively from an earlier date than the rest of the country, artificially rendering its community transmission rates low. It seemed as if the apparently real-time picture was evidence of a stark change of events that talking heads debated as if it were proof and evidence of DeSantis’ underestimated smarts in pushing back against national health policy. Yet the story is far more complicated–and far more Machiavellian–as the pristine blue image of the state–a blue aquamarine that handily recalled those beaches and sun’n’fun for which Florida was long celebrated in the national imaginary-was based on counts from a different time than the dates of cases in all other states, conveying the appearance of salubrity when that was not the case.
Did the state’s office really fudge the public data on its case rates, which it had long ceased releasing daily, using outdated numbers to showcase an apparent contrast sharply evident on state lines? The meaningful legend that might be juxtaposed with the “snapshot” that the delayed reporting of statistics of coronavirus transmission in Florida shaped might be the way that the state had in fact earlier been rocked by successive waves of coronavirus infections, a roller coaster of infections of which the state Governor, who had only recently unveiled a new image for the separate task force of the state that showcased its unique health policies, seemed oblivious, but whose bursts of new cases of infection seemed the bête noir against which DeSantis was forced to tilt in the public eye.
For in taking the emblem of an alligator fiercely guarding its territory, must have loved the data visualization that “mapped”–if deceptively–the improbable case his unique health policies not only separated Florida from national guidelines, as a paradise free from mask-wearing and vaccine mandates. It was a perfect case of how maps lie, which removed him–or his press secretary–from any liabilities, as the map gained a robust afterlife on social media, free from the constraints of real public health data or true comparison of COVID case counts.

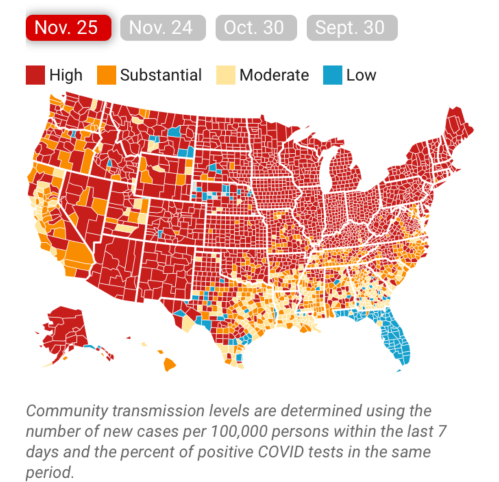
Modeled after the Gadsden flag, the image radiated a stubborn sense of obstinacy as the omicron variant lead to renewed fears of a new spike of coronavirus in Florida, worry that found an odd counterpoint in the map the press secretary took comfort in tweeting out. Yet by Christmas, the gift of the CDC data vis seemed not the gift that keeps on giving at all, as Omicron infections had hit the Sunshine state, proving that its barriers were hardly fixed frontiers.
Although most all Florida had been colored red for much of the summer–amidst concern for the Delta variant, and for “breakthrough” infections–and the new tracker map seemed a lucky break. As the omicron variant leading to rising fear of a new spike of coronavirus in Florida, DeSantis’s press secretary took comfort in an opportune recently issued CDC map to suggest that, low and behold, things had changed, and current COVID visualizations showed “low transmission rates distinguished the panhandle and peninsula, as if the state public health policies had in fact, contrary to recent pandemic history, been doing something right all along.
The crisp borders of low community transmission that seemed to define Florida seemed to be a tip-off, even if the image that was tweeted out was picked up on FOX-TV and other “sources” of right wing or alt right news. The image of a combative alligator defending its territoriality, as a sign of local resilience before fears of rising rates of infection and hospitalization, and is now available at PatriotFlags.
The image of defending a swamp fit DeSantis’ promotion the ports of the Sunshine state as the logjams in ports on the east coast and west coast created problems for transportation hubs in California, Washington state, and New York. “We’re also seeing increased costs, inflation, and higher food prices,” he added. “We in Florida,” DeSantis ventriloquized for the state, showcasing his mastery of boosting public health with the bona fides of a newly minted pro-business eecutive, “have the ability to help alleviate these logjams and help to ease the problems with the supply chain,” with little care for vaccine mandates: In Florida, “At the end of the day, you shouldn’t be discriminated against based on your health decisions.”
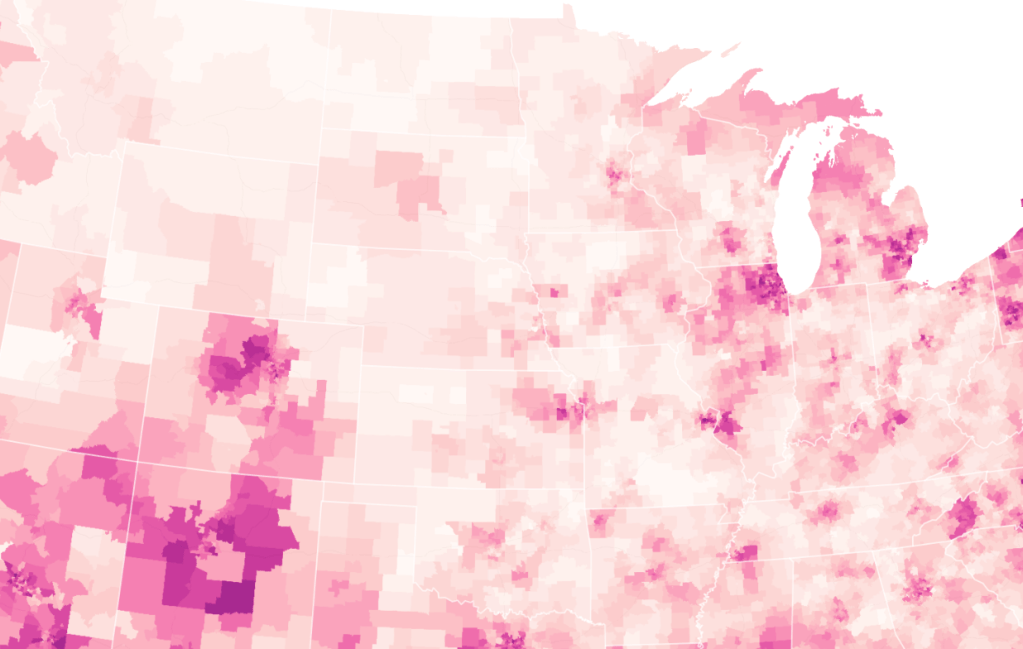
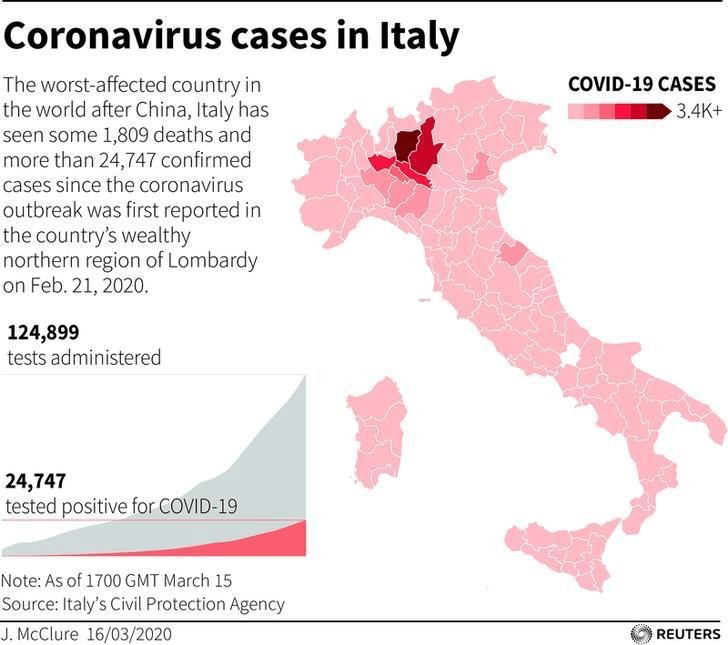
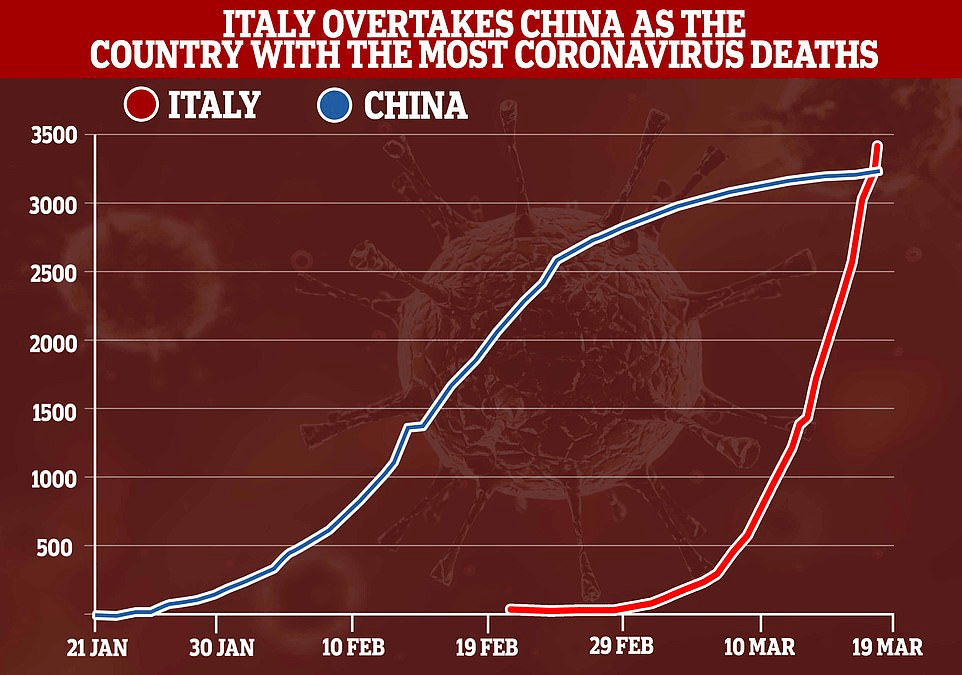
When Christmas did come, it didn’t seem that the state of Florida was particularly bad off in relation to the rest of the nation–but the rising death rates related to COVID-19 dramatically grew across the peninsula in truly terrifying ways, drenching the peninsula pink, and belying those low transmission rates about which Gov. DeSantis’ office was so eager to tweet out.
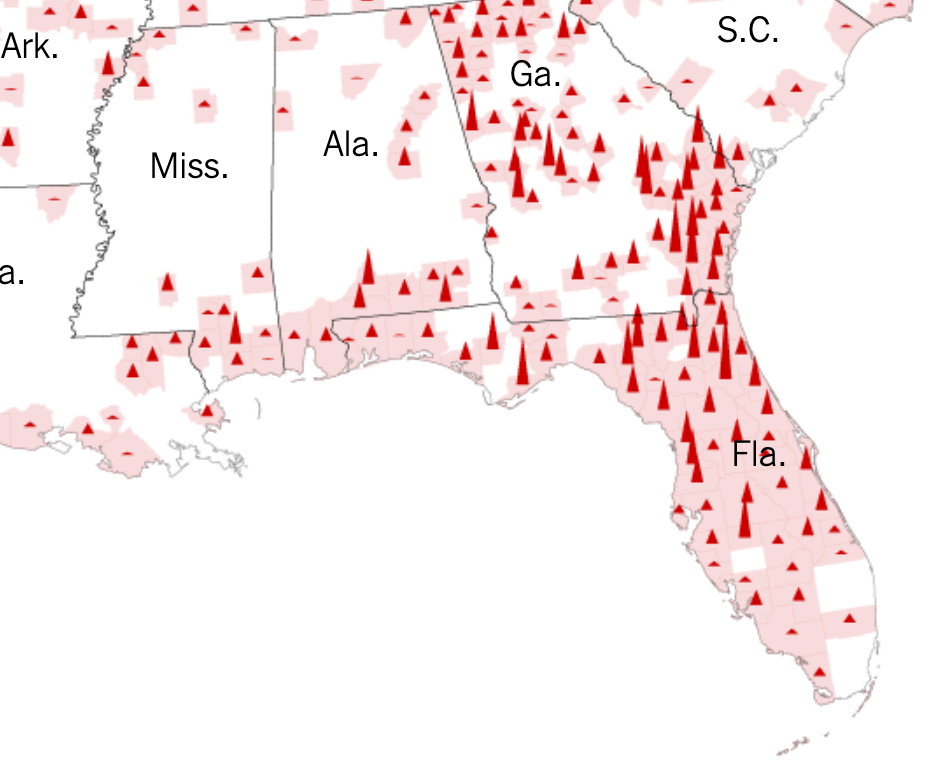
New York Time, December 28, 2021
The level of disinformation is rather without precedent, but speaks in many ways to the hyper-reality of maps of COVID-19 infection that were based on rather dubious and incomplete data providing a rudder in an age of uncertainty. DeSantis’ press secretary tweeted out the CDC map to bate the anti-vaccine commentariat. Arriving pre-Thanksgiving, it seemingly celebrated the arrival of a new state of salubrity: the boundary lines of Florida popped bright blue of unearthly nature not because of what Florida was doing right, but was based on data of community transmission rates at days behind the rest of the nation: state data days out of synch with the national norm created the impression of statistically low transmission rates in the state, and south of the Mason-Dixon line, affirming how things were always better in Dixie.
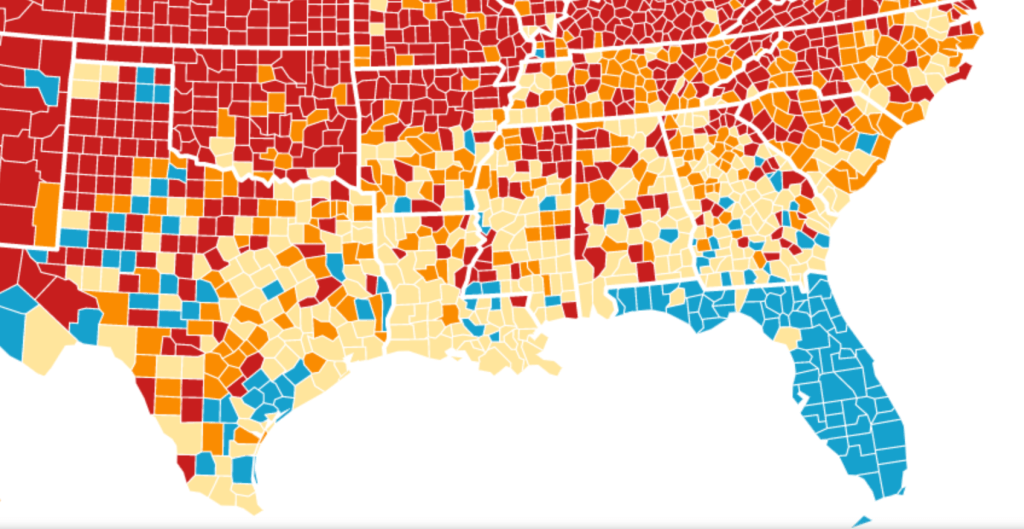
DeSantis had been comparing the low rates of per capita COVID mortality in Florida, despite its large share of elderly, from March, 2021, claiming higher mortality rates for seniors in forty other states had offered evidence that his policies were indeed far more effective than those states that mandated lockdowns and suspended schools, insisting on the benefits of helping businesses and keeping local commerce flow. As FOX news commentators spun the CDC map of community transmission rates as evidence of nothing wrong with fighting masking mandates, or vaccinations.
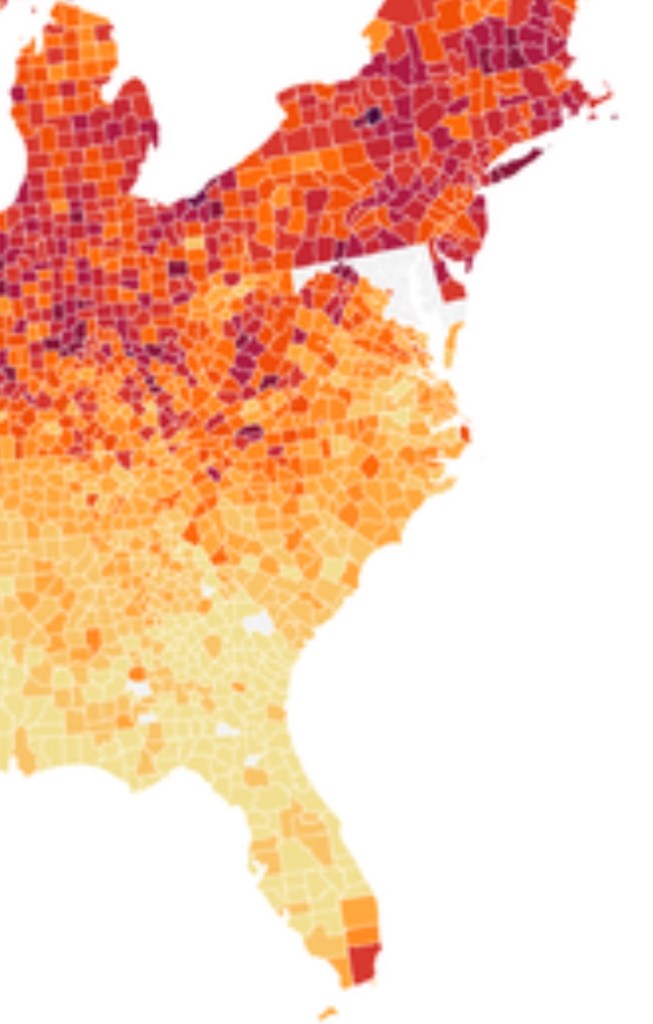
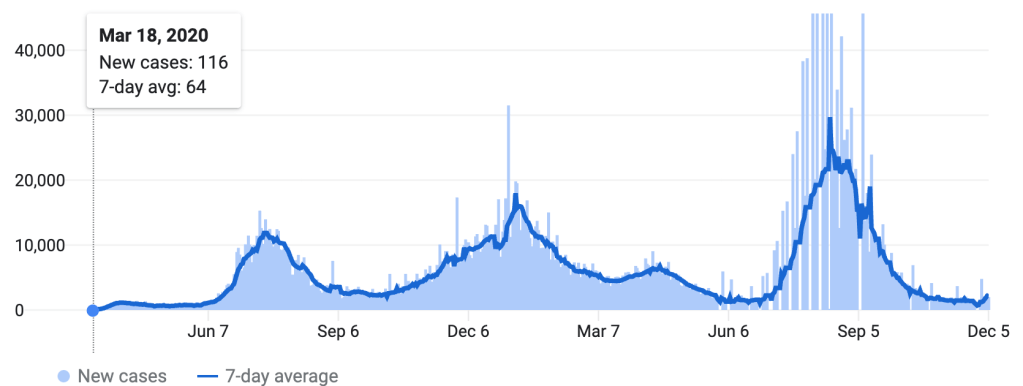
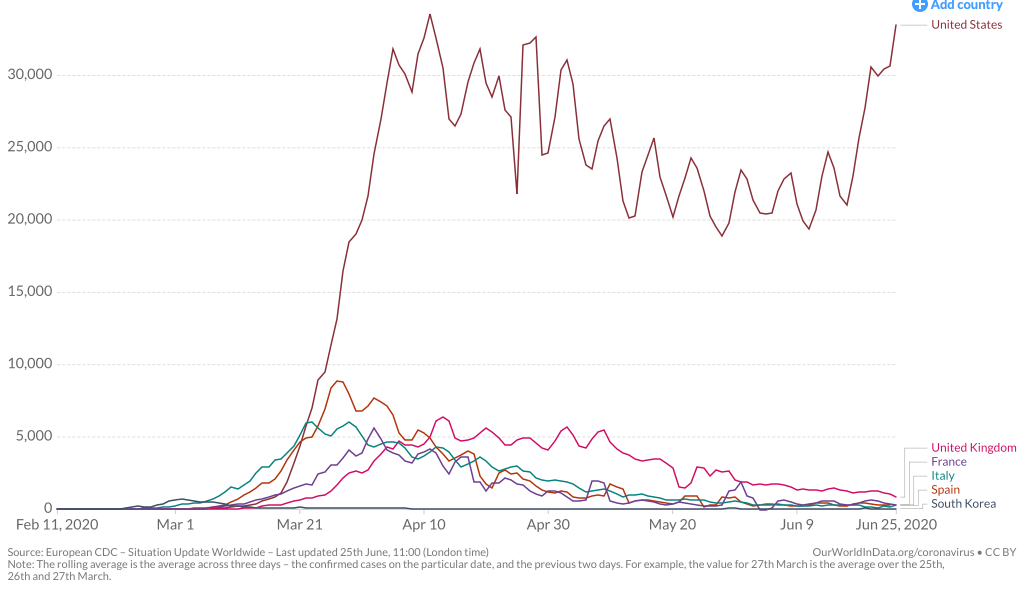
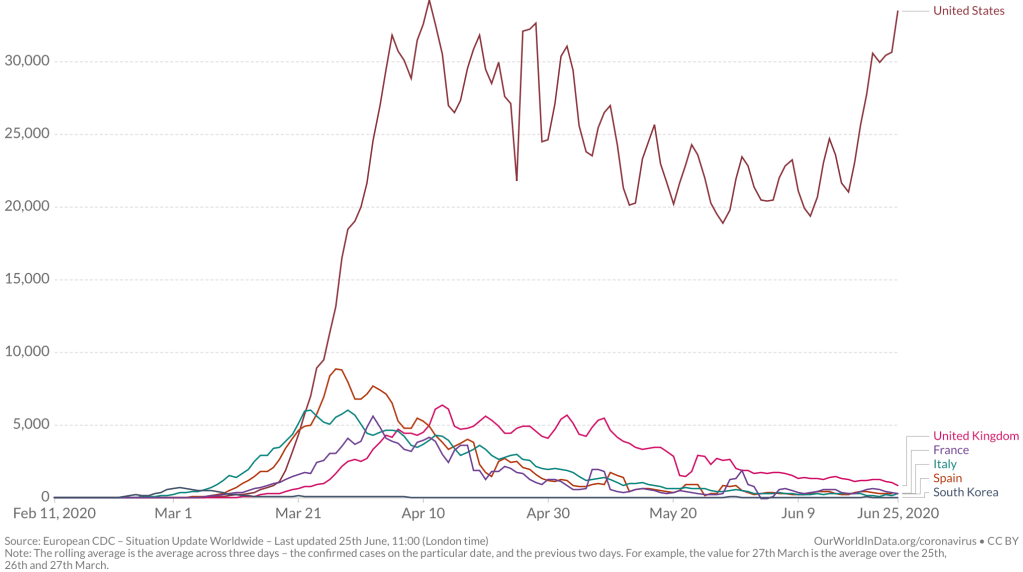
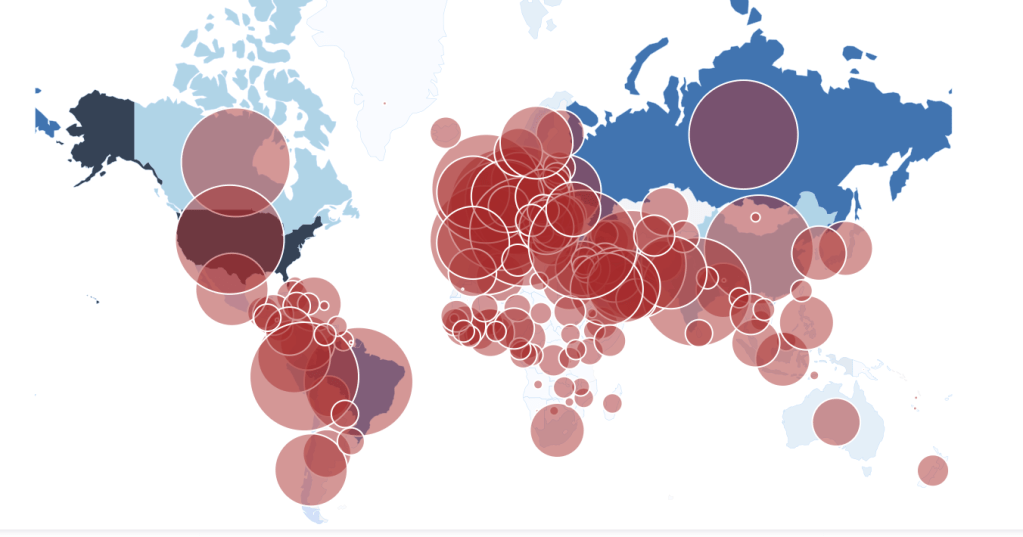
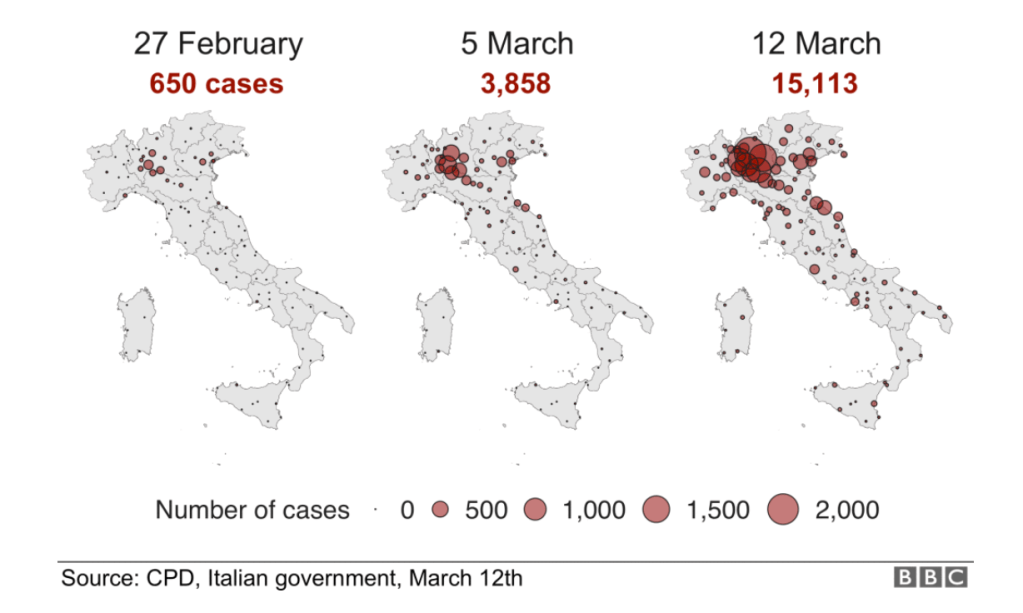
Yet by mid-December, 2021, reality had reared its ugly head. Skyrocketing rates of infection from the Omicron variant proved the folly of asserting any containment of the coronavirus that any policy of one state might so easily fix, as the high rates of infection shifted the panorama of the pandemic, with the fifty millionth case of COVID-19 recorded, and deaths due to the virus across the country topping 800,000–far more than the deaths of the US Civil War, by recent estimates, and more than the current population of Seattle. And if Florida was increasingly as red as the nation, the rise of COVID death rates by the month’s end had effectively eroded all of DeSantis’ suggestion of the benefits of adhering to alternative models of public health care.

If the arrival of the Delta variant had led to the growth of mortality by another 100,000 in two and a half months, the advance of the more transmittable Omicron would stain the whole map red, bridging boundaries and state divides, as thirty three states hosted large infections, with little clear relation to their health policies–save perhaps low population rates and density. By Christmas 2021, national dashboards of infection rates made it clear that Omicron infections advanced not only through the northeast but along the sandy beaches of the Sunshine state.
Yet that single CDC map in the header to this post suggested low COVID transmission rates in Florida was suspiciously more than opportune. For it suggested, lo and behold, starkly lower transmission rates across the panhandle and peninsula, as if the state public health policies had in fact, contrary to recent pandemic history, been doing something very right all along, as DeSantis continued to fence with Joseph Biden’s attempts to devise mandates of mask-wearing and vaccines, all but defining himself as a sort of shadow-government in opposition to the White House, in the manner, say, that now-disgraced Governor Andrew Cuomo and California’s own Gavin Newsom played to Donald Trump, as if voices of stability in the time of need. DeSantis had provided an alter-reality of risk-free no masking or vaccines, freedoms at work and at school, refusing to limit the social interaction and tourism that Florida needs–even accepting cruise lines and offering to provide shipping ports–arguing that reopening was indeed in everyone’s interest, variants be damned: could it be that the CDC was offering a map validating that his policies were working well after all?
Florida boasted low transmission rates, putting the past history of the pandemic in the past, and effectively inaugurating a new news cycle that made this the map to count on and trust–the one dated that very day!–and putting lack of COVID vaccination out of folks’ minds as they booked their family travel plans for late 2021-2. Florida regained its storied status as a site for healthiness and well-being, unlike, it looked at that moment, like the rest of the nation, leading FOX commentators to spin new stories about the long-term success of DeSantis’ absence of clear public health plans.
For although Gov. DeSantis had pulled the plug in June, 2021 on a public-facing COVID-19 dashboard tracking daily updates on cases, deaths, and open hospital beds across the state, inviting those glued to their computers to take two giant steps back from the spate of emergency preparedness that seized the nation from March 2020, the CDC data vis plotted handily outdated data, skewed from rising rates of Omicron that were spooking the nation. As there was no public source of infection rates in the state that was available anymore, the disturbing orange dots that crowded the Florida beaches on the COVID dashboard of the past seemed like it was dispensed with, and the seas calm and skies rosy in a bright blue of low transmission levels–despite DeSantis’ longstanding opposition to vaccine mandates or even public masking across the state.

Instead, the spokeswoman of the DeSantis regime tossed to right-wing news sources a rosy picture of the calm waters of Florida–he must have loved the blue azure that the state was tinted to proclaim low community transmission rates over the Thanksgiving weekend, as if it was a sea of tranquility in a nation that was revving up as word of Omicron spread. (“I hope you make it through Omicron,” the man behind me in Whole Foods said as if a neighborhood sage, finger of the pulse of the rising national pandemic anxiety that had recently seemed safely in the rear-view mirror.)
The CDC image of transmission offered a useful icon of peninsular identity for DeSantis’ media savvy press secretary, who tweeted it out to her almost 22,000 Twitter followers as a dubious ethical claim of the health that the Sunshine State held for all future travelers, according to the current community transmission levels. Indeed, as this detail of the data vis shows, the lower than substantial levels of community transmission in most counties south of the Mason Dixon line would obviate the need for mask-wearing even in public after the arrival of new variants, that the CDC had advised for all counties colored red for high level of transmission.
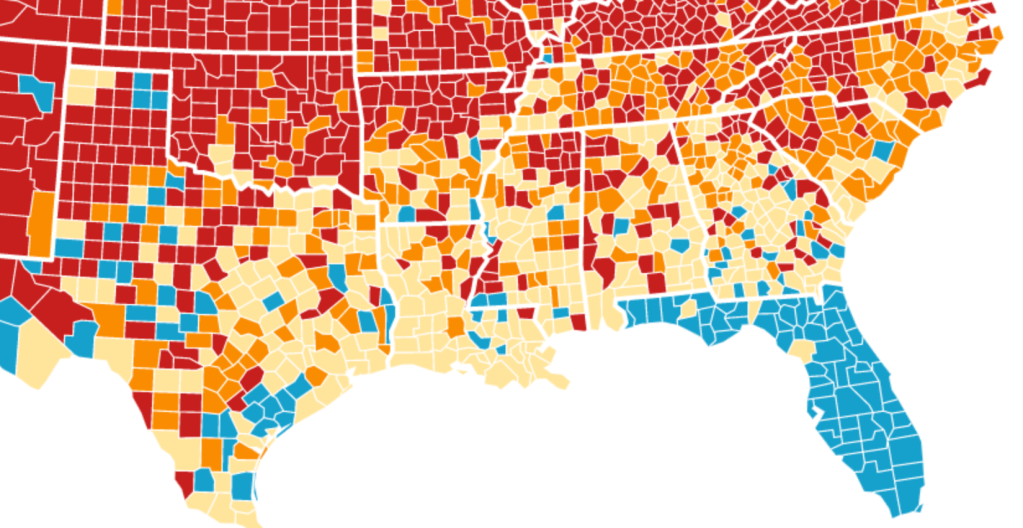
The striking if deceptive visualization that Ron DeSantis’ press secretary tweeted out on Thanksgiving morning had the benefit of depicting the desired “low community transmission” rates that seemed to confirm DeSantis’ attempts to bolster confidence in his public health policies, even if his longtime war on vaccination was not the success story that the map showing the state as an island of relative salubrity was based on an outdated tally of infection rates in the state whose public health policies seemed a concerted effort to sew fears of vaccine safety. DeSantis’ press secretary, who has cultivated a broad presence on twitter since gaining the job, aimed to promote public perceptions of the success of the Governor’s bellicose strategy of vaccine denialism and scoffing diminishment of public health risks.
The data vis was important to tweet out at 6:30 am to hit the national news outlets, because it helped begin or frame a narrative that Christina Pushaw, who had long questioned the value of a “piece of cloth” and long defended the Governors’ criticism of mask mandates. The low transmission rates that cast the peninsula as an island of salubrity amidst national rising fears distinguished Florida as a rare area in which the CDC was not returning to recommend mask-wearing even among those vaccinated–at least per appearances, or a superficial reading, endorsing the exemplary nature of its public health protocol. Unlike most all counties in the nation, prominently colored high-risk red to indicate the return of high transmission rates, Florida (a “red” state) was bright blue as a safety of haven as it had, conservative media argued, weathered out the storm of masking hysteria. All of Florida had been colored red for much of the summer–amidst concern for the Delta variant, and for “breakthrough” infections–and the new tracker map seemed a lucky break.
But the data was off, way off. In fact, the data vis used cherry picked numbers of a previous days that concealed the hight rates of transmission that existed for southern Georgia and all of Florida–as an updated vis of community transmission for the very next day revealed. The shifting image of transmission rates suggested the lag in data that the state was providing the CDC, as well as the greater risk for variants the nation now faces as a whole. But the data vis, entered into the media cycle of the nation, threw many off ground, in its apparent objectivity. Perhaps that was the job of a press secretary: to distribute any image that provided cover for the Governor who had faced criticism for his handling of COVID-19 by fashioning a new media cycle.

So intertwined is travel with the identity and economy of the state, that it was no surprise that the Florida beaches already made it grounds for public health concerns, and the measures during Spring Break, 2021, gave rise to a spike of COVID cases from new variants. In Spring, 2020, infections in Florida had just begun as its beaches filled, and rose again in the summer; but this Spring seemed the textbook case of exactly “what a lot of public health folks have been afraid of.” Increased partying brought rates of infection of a magnitude six times greater, with up to five variants, in the second spike of infections in the state.
The Governor came under fire for his resistance to mask-wearing, social distancing, and toleration of partly open restaurants and beaches, as the coronavirus literally ate into his popularity, and he became something of a “mini-Trump” as Trump’s popularity slid, and many questioned if his positions reflected political expediency and short-term gain, rather than Florida’s interest. But by May he was proclaiming “landmark legislation” banning “vaccine passports” in the state, boasting that the state had, unlike others “avoided protracted lockdowns and school closures in Florida because I have refused to take the same approach as other lockdown Governors,” boasting that the legislation forbade the danger of arbitrary school closures or shutterings, and that “In Florida, your personal choice regarding vaccinations will be protected.” A year after school closures rocked the nation, calling for a rededication of state funds to pay parents for home schooling on FOX, the economic nightmare of state over-reach replaced fears of infection.
March, 2020
DeSantis’ sense of himself as a savior grew in public statements and edicts denying any government overreach, his national ambitions were evident. Arguing that while many other states were just beginning to re-open, Florida was responsibly opening up. He cast the new COVID surge as but a summertime blip, as he embraced “freedom” as a choice of parents by keeping schools open, refusing policies of masking in public, and questioning the wisdom of masking or vaccines, even threatening to not pay county officials who enforce mask mandates, trusting the survival of FLorida’s tourism industry would consolidate his status. Governor DeSantis stood his ground as an ardent supporter of his anti-masking policies and a Trump legacy. He attracted admiration and interest of the communications professional, Christina Pushaw, whose admiration of how DeSantis stood up to “persuasive . . . false narratives” begun in the public press. Pushaw all but publicly identified herself as a new press secretary for the beleaguered governor, whose admiration of his public heath policies, landed her a job but helped to transform the press secretary to an alternative news source, to remap the risk of COVID-19 by a new public health narrative–a narrative that, until recently, had only lacked the right data maps to treat her office’s social media as a new news source.

The rise of infections in Florida echoed the first opening up Florida to tourism in early May, 2020 that continued through June. The recent promotion on social media of the low transmission rates in the state suggest difficulties in balancing a parallel calendar of tourism on which Florida has long relied to the accurate tally of community transmission–a tension that may go back, for Governor Ron DeSantis, to his office’s extended tussles with the GIS analyst at the Florida Dept. of Health who first constructed the dashboard of daily and cumulative infections in the state.
While the Governor had claimed that he would “follow the data” in his opening plans, there were deep concerns that the data was not transparent. When Pushaw wrote a set of attack pieces on the GIS analyst who felt that figures of infection rates were being manipulated, massaged or suppressed infection rates, DeSantis’ Lieutenant Governor promoted it as evidence of “one of the biggest media fails during the pandemic.” DeSantis soon gained a new press secretary, who had essentially applied for the job by praising the skill with which the Florida governor had resisted public masking and vaccines, working to combat the “devastation caused by socialism . . . happening in our country,” and assailed the “big lie” about corruption that a GIS analyst had charged the state. The woman who had worked as an attache in Georgia for Mikheil Saakashvili, now working in Ukraine, might not be a common itinerary to Florida’s Governor’s office, but Pushaw wrote, “If there are any openings on the governor’s comms team, I would love to throw my hat in the ring.” Having assailed the GIS architect of the Dept. of Health COVID dashboard, she offered her services to Florida’s embattled governor to shift attention from COVID-19 infection rates.
After taking the post, Pushaw cultivated a broad social media presence by tweeting some 3,800 times in her first month on the job,–including one arguing watching one’s weight was more protection against COVID-19 than “a piece of cloth” or mask, and promoting the state’s organization for Florida residents of free “antibody infusion treatments” across the state.
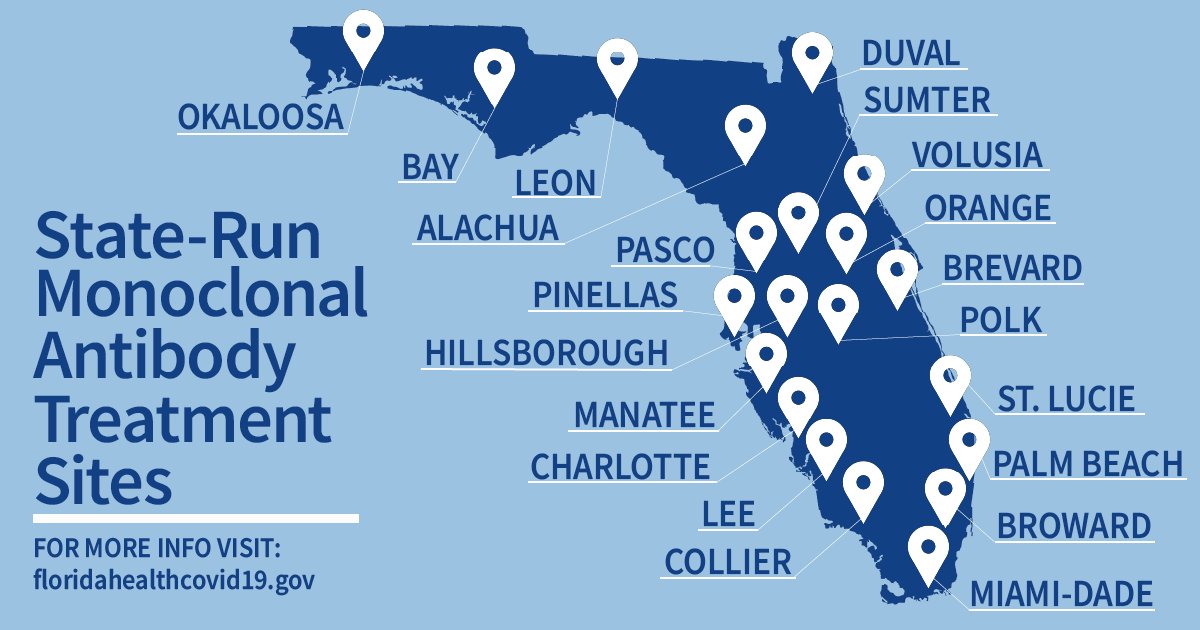
While the map of “state-run treatment sites” seemed to counter the data visualizations of local infection, it tried to set a counter-map to images of level infection or mortality. The notoriety of COVID-19 cases in Florida must have encouraged De Santis’ press secretary to retweet a CDC map dated November 25 that appeared to document low transmission rates in almost all state counties–offering evidence of the healthiness for Christmas visitors. Notwithstanding its Governor’s longstanding resistance to masking and infrequent masking in public spacearding one of the biggest media fails during the pandemic.”. The map retweeted early morning on Thanksgiving Day a shout-out for shifting public perception of the state, as it paints the state as the being sole site of “low” community transmission in the nation, and followed the calls for more praise for DeSantis’ brave strategy of handling the pandemic, since Pushaw became press secretary, both from the Wall Street Journal (Media Ignore Florida COVID Recovery,” October 31, 2021) and Fox News, on which DeSantis echoed Pushaw’s points as he claimed poor media coverage in relation to COVID-19 “deadly” in mid-November, after a rough summer in which 60,000 deaths related to COVID-19 afflicted the state. In early November, One America News Network promoted a special report from this summer (“America’s Governor and Florida’s Grit”) about DeSantis’ guaranteeing of increasing access across Florida of “a life-saving COVID-19 drug” that reduced severe illness.
It was hardly surprising with such lead-up of an alternative narrative on Conservative news that Pushaw seemed to seek to boost the narratives that were launched in conservative media when she retweeted a new data map of COVID community transmission news on 6:30 a.m. Thanksgiving morning as if to target Christmas travel plans to be discussed at the harvest feast that rather highlighted the far lower transmission of COVID-19 relative to the rest of the country as fears of COVID variants multiplied nationwide. The map with national imprimatur showed a drop of community transmission levels in Florida alone, and seemed to offer some back-of-the-envelope evidence that the spikes of previous years in the southern states and in Florida had created local resistance to the coronavirus and its new variants.

The bifurcated image of the nation that showed Florida as, essentially, the sole site of low COVID transmission, would be sure to attract attention and conversation, political ethics be damned. Flying in the face of the longstanding resistance of Florida Governor Ron DeSantis to curtail out-of-state tourism that encouraged him to keep the state open to travel, DeSantis’ new press secretary used the map to show Florida open for tourism, after having weathered three waves of spiking coronavirus infections. Perhaps the state’s poor planning for public health in the past by lifting guidances ofr mask mandates might, DeSantis ventured, create safety in the beaches of the Sunshine State in a winter of variants, as the ‘conservative’ media–Wall Street Journal and FOX–had hinted might be the case.
DeSantis’ groundless claims of safety found somewhat predictable support from FOX commentators in sustaining “natural resistance” to COVID-19 from past exposure, a “natural” immunity better than vaccination, was a data-based strategy, although what sort of data they were using is unclear. (The CDC finds those who had recovered from COVID-19 but were not vaccinated were five times more likely to contract it again than the fully vaccinated.) The conflicts DeSantis’ office seemed to manage between a state economy dependent on tourism and the calendar of increased community transmission suggests a lack of transparency, but also a duplicity based on improvised off-the-cuff diagnoses of a dangerous disease.
The lack of COVID-19 transparency that had been a continuing issue in the state since 2020 had reared its ugly head again, and just in time for post-Thanksgiving Christmas planning. Indeed, the absence of transparency was particularly troubling as we increasingly depend on dashboards, tracing, and positivity rates in grappling with the virus and its ongoing mutations. As the self-declared attack dog of the GOP, Governor Ron DeSantis was by 2021 boosting the dubious concept of “natural immunity against COVID-19” as the forefront of a fight against mandating vaccines for large businesses, exempting from vaccination all recovered from Covid; with full vaccination rates in Florida about 60%, around the national average, Florida ranked twenty-first among states providing at least a single shot to residents. Those already vaccinated in Florida were mostly elderly–a demographic on which DeSantis had dutifully concentrated to provide the vaccine. But many residents in the state, liberated from mask-mandates, were partying, barhopping, hitting the beaches, as masking was unenforced at schools, kept open five days a week, or on cruises–DeSantis promised cruise ship companies that in Florida, they wouldn’t need “vaccine passports.” Bahamas Paradise Princess Cruise Company promised that “safety, fun, and vaccines” were all priorities as it docked in Palm Beach on June 25, having suspended per CDC regulations on March 14, 202, and the fireworks festivies cancelled the previous July 4 due to COVID restrictions were planned again, now with a Cuban reggaeton as a featured guest for the festivities, voluntary masking, as Florida as a state checked out from updating its COVID-19 dashboard, tracking updated cases and deaths across the state.
Governor DeSantis, amidst COVID spikes, emerged as a Trumpian cheerleader standing steadfast in against a “biomedical security state” as COVID infections spiked yet again: “Florida, we’re a free state–people are going to be free to chose to make their own decisions.”
Days after DeSantis challenged Biden’s authority by declaring “We’re respecting people’s individual freedom in this state,” and banning businesses from adopting vaccine mandates–even though the state’s sizable elderly population was demonstrated to be at risk for co-morbidity.
At the same time, a DeSantis spokesperson and press secretary retweeted a rather striking map with CDC imprimatur made rounds on Twitter: the striking data visualization suggested that rates of community transmission plummeted in comparison to the lower forty-eight. While the image depended on the outdated data Florida provided the CDC, a symbolically powerful image as rising alarm about rising rates of transmission injected fear in holiday plans.
DeSantis’ energetic and telegenic press secretary, Christina Pushaw, whose Twitter profile shows her pushing her hair over her head with a smile as if seeking to embody Florida cool, seemed all but to channel a vacation advertisement in her retweet. In promoting the alleged decline in COVID-19 cases from it appeared that Florida had been granted a reprieve as folks were finalizing winter vacation plans in the face of worries about increased infection rates. Pushaw’s tweets had been flagged for vacuuming up right-wing media–a constituency to which she had belong–and had already been suspended once from Twitter in the past. But she retweeted a CDC data vis to promote the apparent decline in rates as evidence that the state provided the secure vacation spot to soak in sunshine this winter after a stressful year.
The bright blue expansed that so conspicuously appeared to isolate the peninsula in a sea of high rates of community transmission of COVID cases appeared to promise Florida offered some sense of shelter from the storm. Yet in spite of all its apparent objectivity, the CDC data vis Pushaw tweeted out on social media didn’t really prove the assertion of Keesman Koury of the Florida Department of Health that low cases of community transmission the data vis registered reflected the “result of our innovative and strategic COVID-19 response that focuses on prevention and treatment,” as if that included no mask mandates or social distancing. As if providing evidence of how much the global pandemic was fed by local bad messaging and toxicity, Pushaw boasted of its safety as if promoting a healthy vacation site in the tradition of the State Tourist Board: “Florida still has the lowest case rate per 100,000 in the entire country and this continues to decrease,” as if the data vis provided cutting edge news, sufficient to rethink the state’s ham-handed response to preventing the virus’ spread.
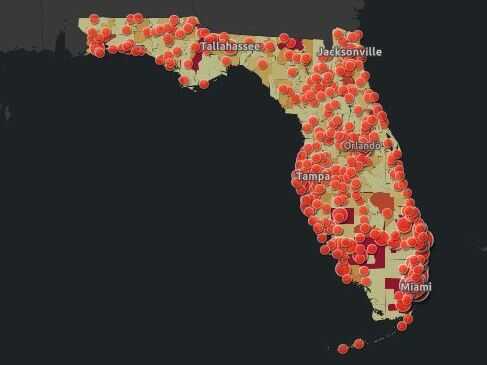
The tweet amounted to outright disinformation–and showed sense of the media savvy of a National Interest journalist turned DeSantis spokesperson known for offensive and off-topic tweets of scurrilous content. Few out-of-staters may have known that she had been accused of stalking the Florida Dept. of Health geographer and data analyst Rebekah Jones, the geographer responsible for having publishing and curating data of COVID-19 infections daily tracking infections, hospitalizations, and deaths related to infection across the state–having built the COVID-19 dashboard to track cases and deaths. Jones had been terminated by Florida’s Department of Health for “extensive, unauthorized, communication” about the dashboard–where she was in charge of answering public questions–and unceremoniously fired May 18, 2020, after raising questions about changes in the publication of data and functionality from May 5, including the combination of tallies of total negative COVID tests and positives, perhaps to lower the calculation of COVID positivity on the dashboard she designed, and the re-tallying of deaths certified as due to coronavirus infections.
As the beaches of South Florida were readying to re-open, Jones, fearing the state fudged public health data irresponsibly, unethically adding negative tests in a false aggregate–even if conducted for the same person–to diminish the ranking of positivity, even as DeSantis proclaimed he was “following the data” in re-opening. Months earlier, Jones had created the dashboard and apologized for the lowering of mortality rates announced per Florida’s Dept. of Health, in the course of reclassifying many coronavirus-related deaths, as the Dept. and adding fewer deaths despite rising mortality rates in Florida to deaths verified as related to COVID-19. The state argued it would “continue to provide the most up-to-date information to arm Floridians with the tools and knowledge necessary to flatten the curve,” but seems to have shifted the nature of its total counts of deaths or indeed of positive cases of infection. But, unlike the state dashboard, Jones showed the density of confirmed COVID infections and the few Florida counties which, by her count, ready to reopen.
1. The data aggregated on Jones’ alternative dashboard suggested that rather than the curve flattened, only two of sixty-seven counties in Florida met the state’s established criteria for re-opening. She complained Florida’s Dept. of Health had wanted her to delete the report card of infections per county, as it showed “that no counties, pretty much, were ready for reopening;” FDOH didn’t want that visible on the dashboard in ways that would “draw attention” to an inconvenient truth, she said in mid-June. (At the same time, the state had witheld data on deaths certifiably related to COVID-19 at nursing homes and assisted living facilities, unlike other states, to keep figures low.)
As the data guru in charge of publishing the data, Jones would be expected to be central to any public health work that was based on the data. But she alleged her refusal to lower the state’s positivity rating to allow it to meet its target for reopening led her to be dismissed: as the state became an epicenter for infection in March 2020, the state faced increasing pressure to meet goals to be “ready to open” for the summer.

Despite noting the “dramatic changes” on the data portal of concern back in May, 2020, Jones, whose dashboard had long been trusted as a source, seemed to feel it had swung beyond her control: she would only say in early May, “I helped them get it back running a few times but I have no knowledge about their plans, what data they are now restricting, what data will be added and when, or any of that.”
The long familiar site which Florida residents had used to orient themselves to daily updates of county-by-county breakdowns of new and total positive cases of COVID infections, virulence, hospitalizations, and deaths had shifted,–about a month before infections would peak–
–and infections in the state broke previous records, adding nearly 9,000 new cases in a new daily record by June 22, 2020, before the arrival of the Delta variant.
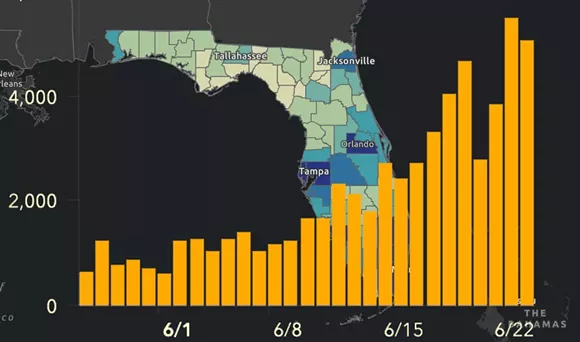
The numbers of positive cases for state residents grew, as hospitalizations, during that very summer, when they ballooned, and multiple counties in the state grew deep blue.
As if in response to what she contended was an unmerited ouster from Florida’s Dept. of Health for failing to fix datasets, Jones quickly founded her own alternative “rogue” informative COVID-19 dashboard, Florida’s Community Coronavirus Dashboard.
2. While DeSantis had outlined, under the approving eyes of then President Trump, plans to re-open the state by placing “public health-driven data at the forefront” along fixed “benchmarks,” his data guru insisted her refusal to be part of promoting “misleading and politically driven narrative that ignored the data;” she constructed an alternative dashboard showing only one of the sixty-seven counties in the state revealed sufficiently low positivity to warrant reopening or easing restrictions on social distancing. The exclusion of positive antibody tests on the Dept. Health website was clarified on the new site, which aimed to be far updated daily and far more user-friendly when it appeared in June, 2020, and tracked the rise of positive cases that summer, adding increasing features of legibility and of tracking change over time.

The new site foregrounded total “COVID Positive People” detected in both PCR and Antigen tests in running tallies, listing new positives from the previous day, running counts of recoveries, and available hospital beds beside a county-by-county breakdown, the dashboard offered a far more synthetic fine-grained map of the COVID-19 ground-game of public health to grow public trust. The rival dashboard that debuted in mid-June aimed to show accurate geodata of “what’s going on in a straightforward, nonpolitical way,” FloridaCOVIDAction.com synthesized publicly available open data, mined from state reports but not reported straightforwardly on state-run websites.
As it became clear that the data for which Jones and a group of epidemiologists had been never incorporated in DeSantis’ vaunted plans to rely on the data in plans for re-opening the state; reopening brought a five-fold surge in COVID infections by mid-July. The expansion surpassed the rate and number of Covid-19 infections than any other state in the pandemic, breaking records for the highest number reported in a single day–15,300–or in New York in early April, during the worst outbreak in the city. The wave, which might well have been prevented, strained hospital and treatment by antivirals. It called into question the logic of DeSantis’ reopening plans, or how much he had relied as promised on health-driven data, but a blind adherence to the sense of “best practices” that could allow the economy to be open, beaches and restaurants stay open with adequate distancing, and schools not be closed–meeting short term demands and needs for the summer economy, but sewing skepticism.
The state in fact seemed to lack even sufficient testing to measure the scale of the outbreak, even as he reopened the state at a far faster clip than New York or California, re-opening all gyms, bars, indoor dining at restaurants, schools, pools and salons and ending stay-at-home orders but a month after they went into effect, to welcome tourists to the state from Memorial Day, increasing the risks to the state’s older residents greatly, before closing the bars in late June. By November, after an other rise in COVID cases ran through the state, Jones’ public message to the Florida Dept. of Public Health to “speak up before another 17,000 people are dead” as the dashboard stood at 17,460 COVID-related deaths in the state, law enforcement served a search warrant at Jones’ home, guns drawn, seize the laptops from which the former GIS manager of the Division of Disease Control and Health Protection ran the alt dashboard–“all my hardware and tech”–seven months after her firing from the Dept. of Public Health.
The dashboard of rising COVID infections released on an ArcGIS platforms was a bombshell that placed her in the public eye–and was regularly updated. The alternative website seems to have led to her attack as a discontent “rogue” rather than a whistleblower in the national news. Its release lead to subsequent national media slamming of Jones in conservative media as a serial social media abuser, as outlets tagged the former public health official as a “super-spreader of COVID-19 disinformation,” to defuse her own charges of community transmission. Jones was charged of being guilty of having openly invented lies “about Ron DeSantis’ Press Secretary” using social media to pedal pandemic falsehoods. @GeoRebekah temporarily de-platformed on Twitter, Pushaw crowed that her suspension revealed Jones’ untrustworthiness and abuse of the medium, calling it “long overdue.” No doubt infuriated and flustered by DeSantis’ own consistently relax and dangerously reckless policies on keeping schools open and removing COVID protection policies, Pushaw must have been not only frustrated, but a target of DeSantis’ ire.
Pushaw went further by attacking the GIS systems manager as nothing less than “the Typhoid Mary of COVID-19 disinformation,” echoing the bombast of the DeSantis regime. DeSantis and his office dutifully applauded Jones’ temporary suspension as evidence for her duplicity, as guilty of “defamatory” statements and a “COVID super-spreader,” happy to see her public profile reduced. Comparing the systems manager to an Irish-born cook whose asymptomatic infection spread to her employers what was known as Salmonella oddly served to demonize her as an immigrant carrier of disease, echoing Trump’s obsession with “foreign” origins of COVID-19; it shifted attention from dangerous mortality levels in the state, and gestured to an era when the pathogenic transmission of salmonella was not understood, more than inadequate responses of the Governor’s office to three waves of COVID-19 in the state. A leader who had and would repeatedly cultivate “strongman tactics” in a dangerous time, as Ruth Ben Ghiat recently noted as this blog was first written, DeSantis performed a version and vision of leadership that seemed to establish himself as an autocratic leader of Florida, with a proposed a new Florida State Guard to assist the National Guard in public emergencies, that he would oversee as a state militia, that could act “not encumbered by the federal government” or federal regulations, from federal masking policy to vaccination mandates, and banned vaccine mandates or masking in public as unsafe and unscientific.
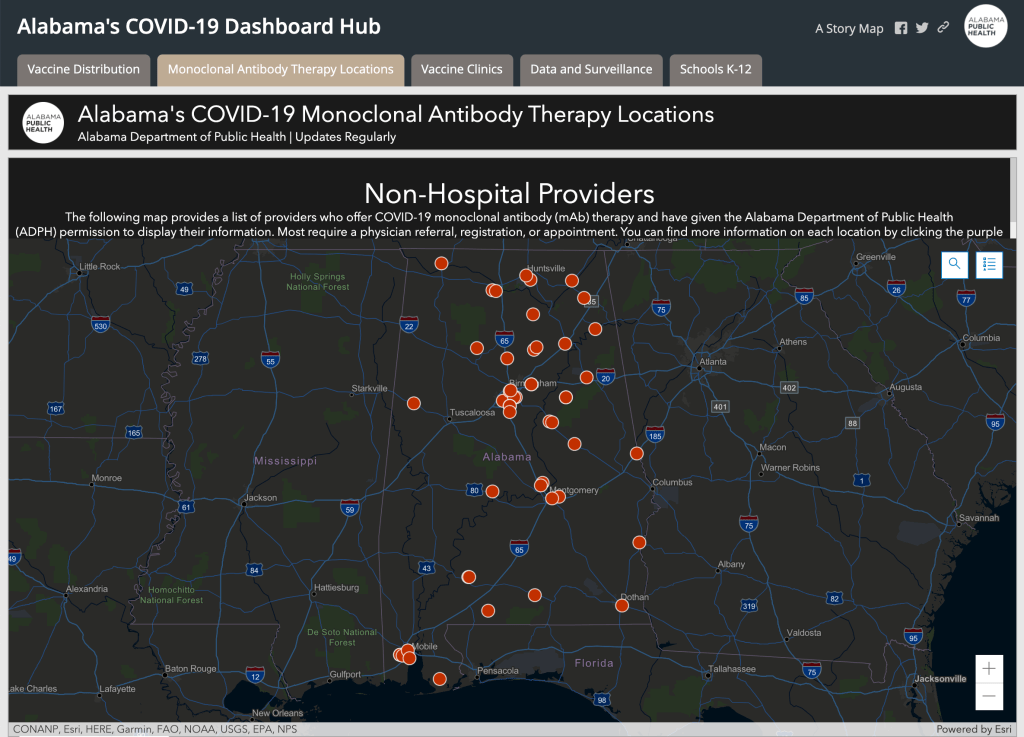
DeSantis chose another official to be an attack dog to step up vaccine disinformation. The campaign of disinformation continued DeSantis had appointed a surrogate “State Surgeon General” who stood beside vaccine skeptics who encouraged misinformation from claiming the vaccine altered your genetic RNA to a lack of scientific consensus in its value. Surgeon General Ladopo spread dangerous COVID denialism, instructing the public “to stick with their intuition and their sensibilities,” demeaning the public health value of the vaccine a misguided “religion” and emphasizing the monoclonal antibodies treatments DeSantis has vigorously promoted in the place of vaccines–and indeed as an alternative public health policy. In so doing, he mimicking the public health maps like Alabama’s “COVID-19 Dashboard Map” that foregrounded Monoclonal Antibody Therapy (mAb) therapy as a counterpart to Vaccine Distribution in an ESRI Story Map; Alabama’s Dept. of Health boasted a 60-70% success rate at “preventing high-risk patients” from being hospitalized–a strategy of off-loading any public health care policy or plan.

If we are approaching a time in the history of COVID-19 when our fears of catching the disease may soon be replaced by an acceptance that we may become infected, and will manage that infection, the hope to navigate infections that would be more severe among the unvaccinated populations suggest a tinderbox that will require an armed guard of the sort DeSantis has imagined as running when he announced in Pensacola his plans for a military unit with uniforms tagged “FLORIDA” rather than “U.S. ARMY” from a podium bearing the sign “Let Us Alone” that echoed the “Don’t Tread on Florida” sign displayed at a special October session of the state legislature to counter federal COVID-19 vaccine mandates. The curious unveiling of a “civilian volunteer force that will have the ability to assist the national guard in state-specific emergencies” seemed design either in case of another surge, or to support DeSantis’ distinctive public health policies. The banner “Let US Alone” first displayed in the 1841 inauguration of Florida’s first Governor, William Moseley, was a cause for celebrating the independent health policies in the state, which had by then reached the third-highest number of infections in the nation–3,730,395.–and the third-highest number of deaths, 52,647.
The image shard of a combative alligator defending its territoriality, Florida’s own Gadsden flag was unveiled at a press conference speaking out against vaccine as the new logo of the state: the alligator with gaping jaws, ready to attack or defend its ground, was tweeted out on October 21, 2021 by @GovRonDeSantis as a sign of resilience and power in the face of the fear of rising rates of infection and hospitalization, and is now available at PatriotFlags. The image of defending a swamp fit DeSantis’ promotion the ports of the Sunshine state as the logjams in ports on the east coast and west coast created problems for transportation hubs in California, Washington state, and New York. “We’re also seeing increased costs, inflation, and higher food prices,” he added. “We in Florida,” DeSantis showcased the pro-business benefits of his health politics with the confidence of a newly minted executive, “have the ability to help alleviate these logjams and help to ease the problems with the supply chain.” In Florida, unlike Biden’s America, DeSantis proclaimed as a rallying call, “At the end of the day, you shouldn’t be discriminated against based on your health decisions.”


The Gadsden Flag, beloved by separatists–and displayed at the door of a neighbor of mine in Berkeley with the slightly menacing words “Don’t know what it is? Look it up!”–has of course become a treasured emblem of the right, and Patriot groups, as well as militias, and was flown on the U.S. Capitol briefly on the morning of January 6, 2021.
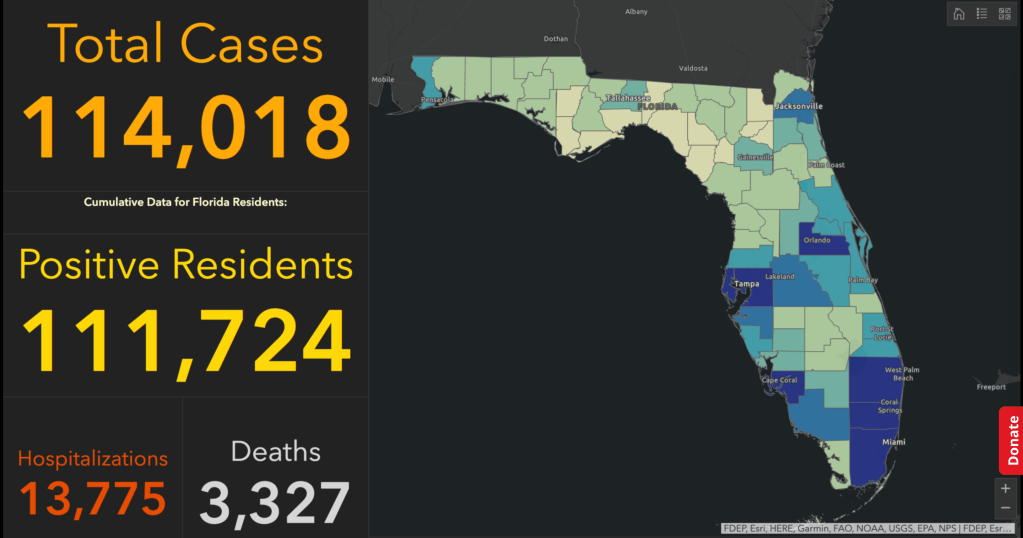
3. Pushaw and Jones had a long history of entanglement. The ways that their fraught relations determined the battles over the local messaging on the pandemic remind us of how its global spread was brewed in the toxic channels of local miscommunications about public health. Governor DeSantis had only hired Pushaw as a press secretary, per WaPo, after realizing public messaging on COVID-19 crucial to his public image. The Florida Governor seems to have been especially keen on Pushaw’s exposé of Jones’ “big lie” about DeSantis’ reticence in releasing total counts of positives, long before he restricted state dashboards to weekly updates of limited information by June, 2021, as total cases of infection surpassed 1,7783,720, creating a crisis in calm as the state faced a second spike. By then, Florida ceased reporting deaths or infections daily to the CDC, making them hard to tally with regularity, and shifted the format to weekly tallies of vaccination and infections, as the “surveillance dashboard” radioed staying away from the beaches around Daytona Beach or from Fort Lauderdale to Miami Beach, even as new cases seemed to decline, and hospitalizations grew, as the daily tabulations of resident deaths and COVID positive suddenly ceased.

The articles Pushaw had written attacking Jones’s whistleblower status may have encouraged a long-running conflict that led her to be charged with “computer crimes”; Jones’ charged the press secretary with having stalked the GSI analyst obsessively and aggressively, slurring her reputation after she was fired, allegedly for insubordination for refusing to undercount infections and magnify the number of people tested. The vindictive attacks on the data analyst obscured the problems of reduced clarity of replacing the daily updates on which viewers had relied with weekly tallies.

The Surveillance Dashboard offered a comprehensive running count and cumulative tally that Jones was charged with having crashed before her dismissal from the Dept. of Health, six months before the police entered her house in December, 2020, weapons drawn, to seize her computers as the novel coronavirus was spreading widely across the state.
Despite the value of allowing state residents to orient themselves to the spread of COVID-19, Jones disturbingly suggested the state was playing fast and loose by manipulating data of infection rates by slimming counts of positives by omitting almost 10,000 antibody tests from its tally. Yet by June 22, 2020, twice broke records for single-day infections in a week: the state dashboard of daily data announced a new record of nearly 8,000 infections and 13.5% positivity rate–a critical number just over the early baseline for re-opening of 10% positivity–even if the WHO baseline for reopening was set in May, 2020, in preparation for summer, at 5% or lower for two weeks. Playing fast and loose with time-stamped data in troubling ways, DeSantis assured the public in mid-June as positivity grew that journalists should realize the past was more important than the present in his allegedly data-driven response, rather than the policies he had adopted: “the main thing is just for folks to look, in May, if you remember end of April, May all the way through, you know coronavirus was relatively quiet in Florida. You had manageable cases. Our positivity rate was 4 or 5 percent consistently.”
Only in late June, 2020, was a Public Health Advisory issued that back-tracked on Governor DeSantis’ longstanding objections to preventive measures like public mask-wearing, social distancing, and caution. In fact, some 20 million cloth masks distributed statewide that “all individuals in Florida should wear . . . in any setting where social distancing is not possible” and social interactions limited for all over age sixty-five. The cautionary tone was not alarmist, keeping bars and restaurants open in the sixty-four counties it defined as in “Phase 2,” and allowing all retail businesses and gyms to operate at full capacity, entrusting their clientele to practice social distancing from one another, as part of a “plan on public recovery.

Yet the Governor, in his wisdom and care for his pubic perception , issued an Executive Order Affirming Freedom to Choose emulating the then-President, by June 2021, after school boards considered adopting mask-wearing mandates for their students, as a part of schools being “open for instruction” since the summer of 2020, noting how “masking may lead to negative health” and the CDC “guidance . . . lacks a well-grounded scientific justification.”
By August, as the weekly counts of new infections surpassed 110,000, according to CDC data the most in any state of the country, Floridians missed getting daily updates on the counts of infections per county. The old regularly updated dashboard has became a focus of public attention in what seemed a laboratory case of an unfolding public health disaster–DeSantis had phased out county-by-county daily breakdowns as he issue weekly tallies, having argued that the state had rounded the bend, and removed the regular daily updating of dashboards on which Floridians had long relied on to orient themselves. Age breakdowns and a geographic distribution by county–features of the old dashboard–were no longer available, even as schools were reopening, parents deciding on vaccination and masking, and public trust frayed.
Since the escalating records of early summer cases in 2020, the state dashboard had provided a familiar breakdown of infections, offering real time information based on age in a county-by-county breakdown that all of a sudden wasn’t there as a guidepost for local decision at a critical time, once it had been removed.
More crucially to this post, the constraints over how much information of COVID transmission was publicized–and how accurately it was compiled–suggested that DeSantis’ office commitment to ensuring the calendar on which the state’s economy for tourism depended had displaced the monitoring of a calendar for community transmission. By June, 2020, the Florida Dept. of Health substituted weekly COVID tallies in place of the daily breakdown and count that Jones had worked, explaining that the state wanted to streamline information and reported daily case data to the CDC. The new weekly dashboard failed to orient users to a geographic distribution of COVID-19 or what counties infections had occurred, so prominent in the old dashboard; it provided little data that could be drilled down into, by abandoning a county-by-county distribution and dropping the stark visualization of state counties as a “third wave” of COIVID-19 infections hit in 2021, and DeSantis mused that the county-by-county breakdown might be useful to some.
DeSantis proclaimed the state had turned the bend. But as Florida led the country in newly confirmed cases in early August, 2021, folks wondered why the daily dashboard of old was no longer readily available as a tool of visualization, worrying that the daily updates were pulled by the Governor’s office prematurely in June, as the pandemic led to more hospitalizations in the state than ever before, but the Governor’s office, rather than offering public health data to state residents, asked for patience “in returning to normalcy”–even after twenty-four days with over 1,000 new cases discovered daily. And in tweeting a map of low transmission rates in the post-Thanksgiving days, claiming COVID cases had begun to “bottom out in Florida,” while they started to peak nationwide, Pushaw seemed to seek to clean up Florida’s public image, by directing attention on social media to an alternative reality that may have benefitted a map that rendered rates of community transmission taken, albeit a map that had benefitted from the new timeline at which Florida was releasing data to the CDC. Indeed, the release of figures of community transmission at different times from the country seemed to offer evidence of how clear-headed policies had kept local transmission rates low, even if the data ws comparing apples and oranges.
The tweet seemed to seek to erase memory of those dashboards of the recent past, that might well have kept tourists away from Florida, due to high positivity rates. The apparently credible picture showing low risks of viral transmission statewide was a retrospective reprieve of sorts for the inexcusably poor public health policies of the past. Although the CDC had updated data on community transmission for the nation, the state received a rather convenient break: for local data had ceased to be updated with much regularity for Florida, compared to the rest of the union, rendering its counties an almost continuous bright blue. Pushaw’s early a.m. tweet was the perfect graphic for her smiling Twitter profile, which recalled the vacation ads of old that promoted the salubrity of the state’s sunny beaches.
The imaginary fault-line that seemed to isolate the panhandle and peninsula as a sight of purity and safety was itself a creation of the lag in the reporting of state data, rather than reflecting a break in community virulence or the “bottoming out” of COVID cases. But the implication that Florida had suddenly become an area of low community transmission reflected cherry-picked data crafting a false comparison between apples and oranges, so to speak, since the state’s data had stopped updating as the rest of the country suffered from rising rates of COVID-19. Was the absence of inclusion of available data on the national COVID data tracker a mistake, or a convenient untruth of deeply unethical nature?
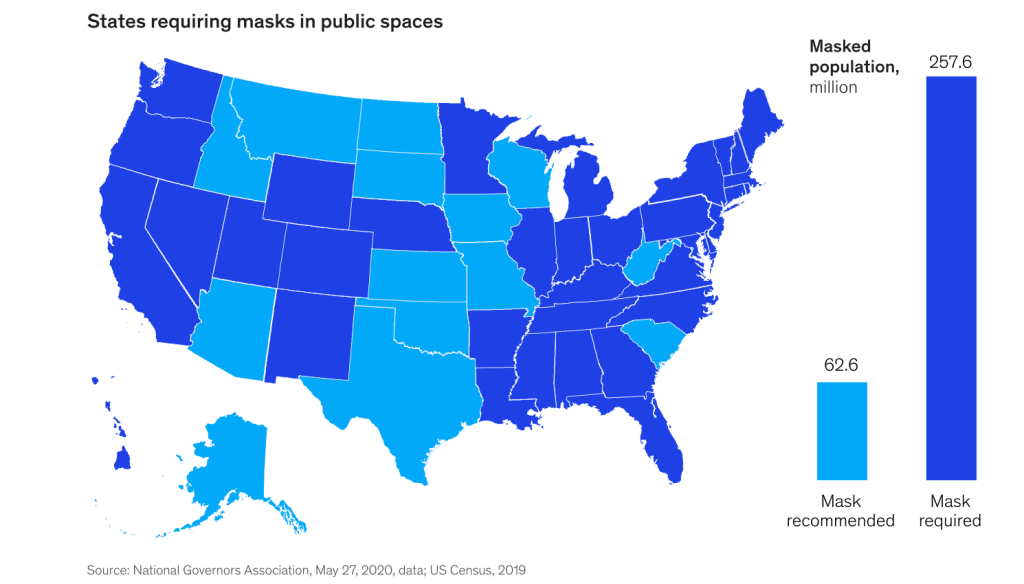
The maps of cases, infection levels, and fatalities, had been if only six states have mask-wearing mandates for the vaccinated and unvaccinated, whereas in 2020, forty-three states had adopted them, the low levels of transmission seemed to promote an image of azure seas across the peninsula that was oddly akin to the images promoting the Vacation Land U.S.A state from the mid-1950s, presided by a beneficent smiling sun, whose rays boded health for all–where the sun was able to be drunk to good health daily in the state’s unofficial elixir, fresh orange juice. Concerns about the continued popularity of winter beach destinations during the rise of the new Omicron variant may have been leading many to rethink their vacations, but the data vis was dropped at a strategic time to plug the beaches’ open space as a space for rejuvenation, a ready get-away for those seeking escape from COVID stress.

State of Florida Tourism advertisement placed in National Geographic, 1952
The couple romping through the surf promised escape in a “lovely peninsula, with its 30,000 lakes and 1,400 miles of mainland coastlines, which is continuously cooled by refreshing [ocean] breezes” is removed from the fears of coastal erosion that recently reared its heads in the collapse of the Seaside FL towers. But the coast beckoned as a site of sociability, for many who had been spooked by the rise of COVID-19, the beach offered an image of health in ways that rehabilitated the classic cinematic myth of the sunshine state of ocean fun.

The past imaginary was one of all carefree abandon, promising a year-round vacationland, outside of the normal flow of time or the seasonal change–as the 1954 advertisement put it, “WARM in Winter–COOL in Summer!“–that would produce “a fabulous state of well-being.”
The “extra special” nature of Florida as “one of the world’s greatest concentrations of fun facilities” was tied to its beaches, but stretched “border to border,” mapping a vacationland free from worry. Was Republicans’ not readiness of to nix the federal budget over mask mandates, and resist previous mandates on vaccination that would buck the federal advisory that folks “resume activities without wearing a mask or physically distancing” in areas of high or significant transmission risks, mandates for the unvaccinated only existed in reliably “blue” states–California, Connecticut, and New York–where they did not face legislative pushback, and the mask mandate for all only applied to those island territories with uncertain public health infrastructure–Puerto Rico, Guam, and the U.S. Virgin Islands–where an outbreak could be devastating, and where Democrats acknowledged the public costs as critical, from Hawaii to New Mexico to Nevada to Illinois, where the COVID scare remained fresh in memory.
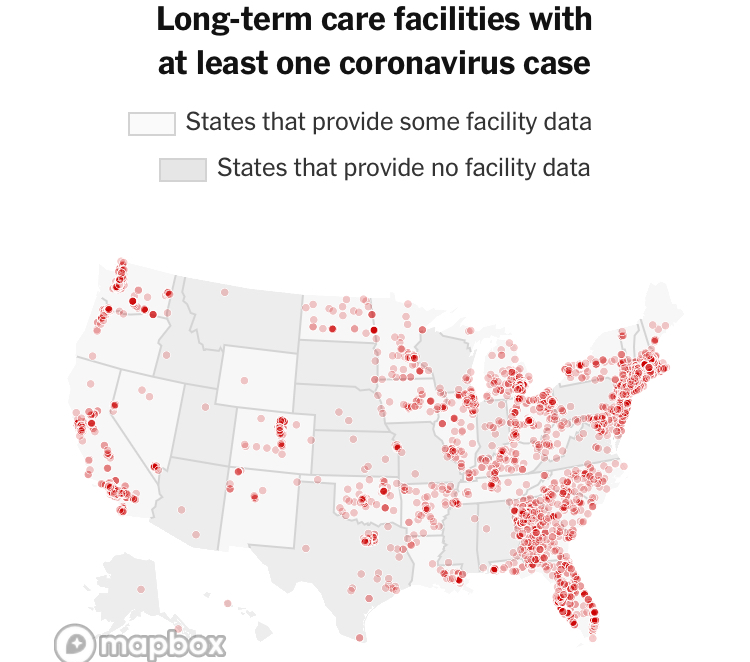
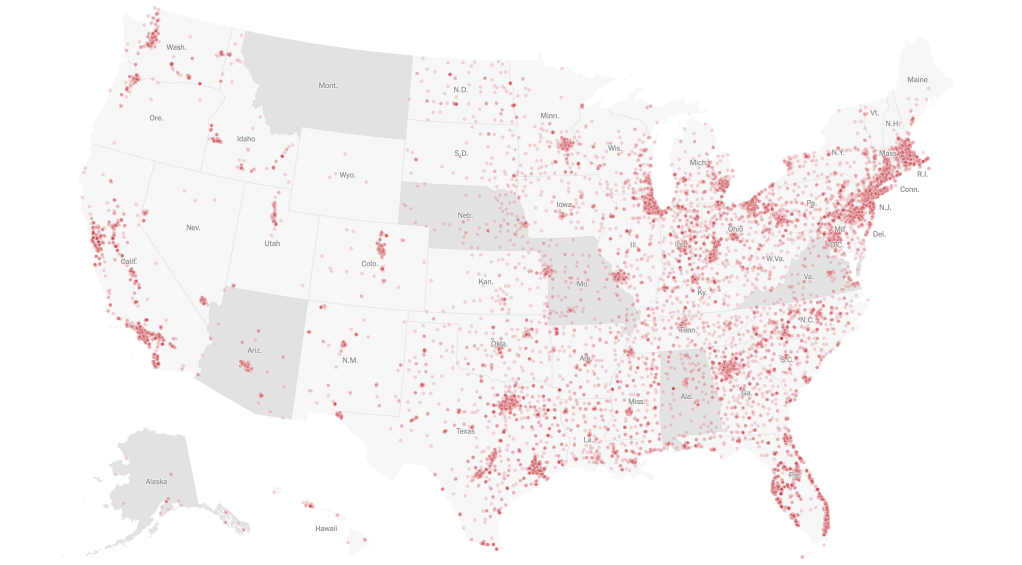
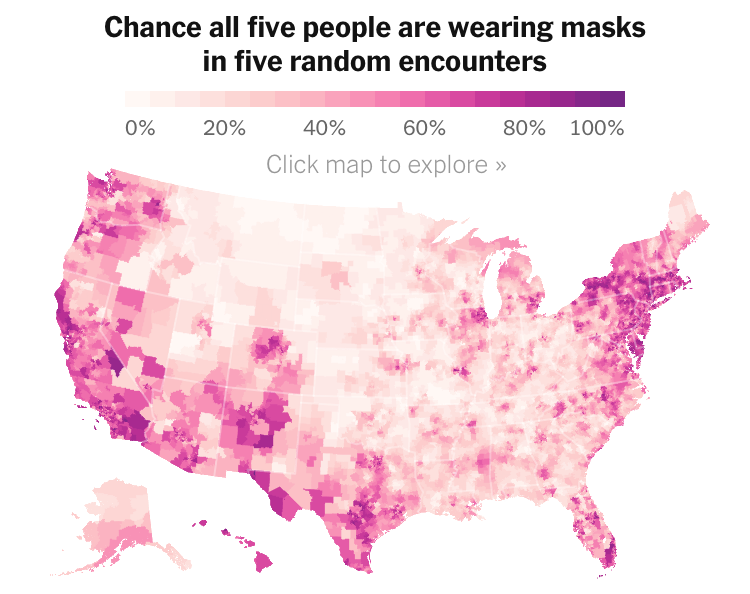
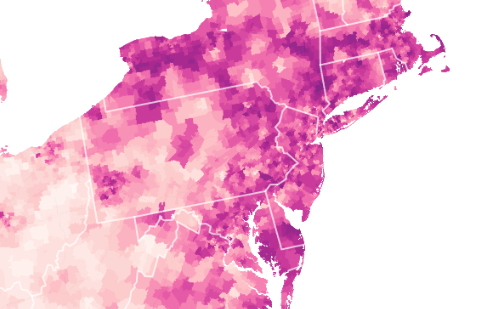
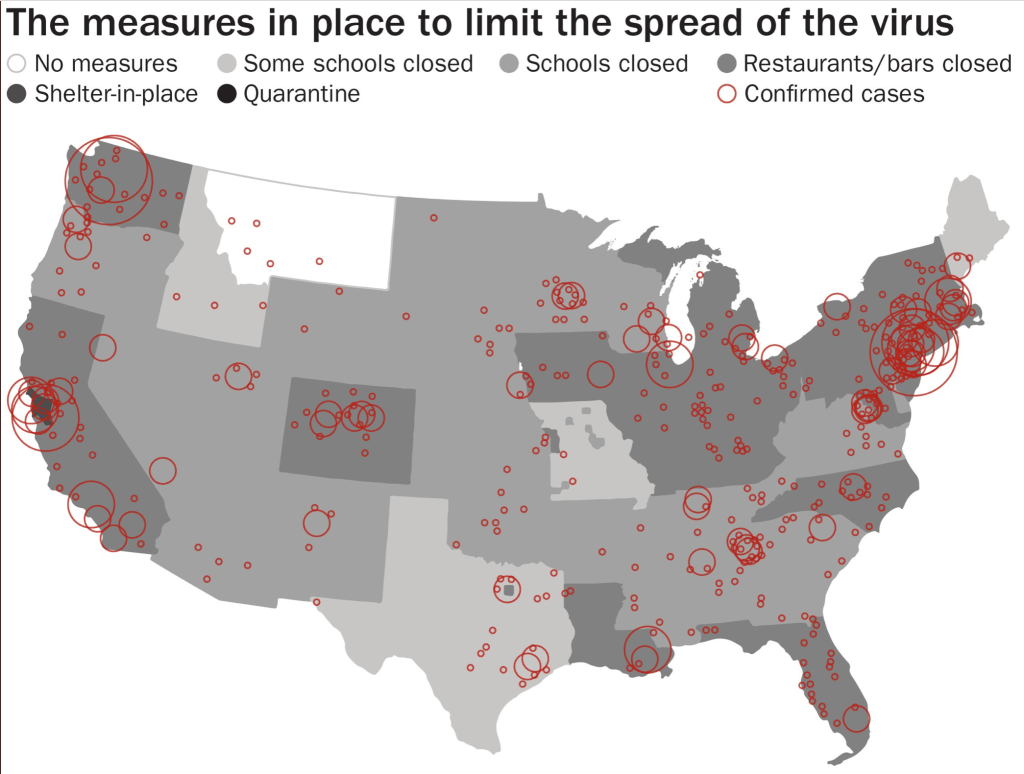
Florida was long an outlier of mask-wearing, especially on its beaches, per this classic Mapbox data visualization of the likelihood of meeting masked friends in public from mid-July 2021, that reflected the split sort of realities with which the nation had been confronting COVIDThe rarity of spotting mask-wearing in midsummer 2021 was super spotty in the Sunshine State, especially on its beaches, in a state seemingly torn by parallel realities.
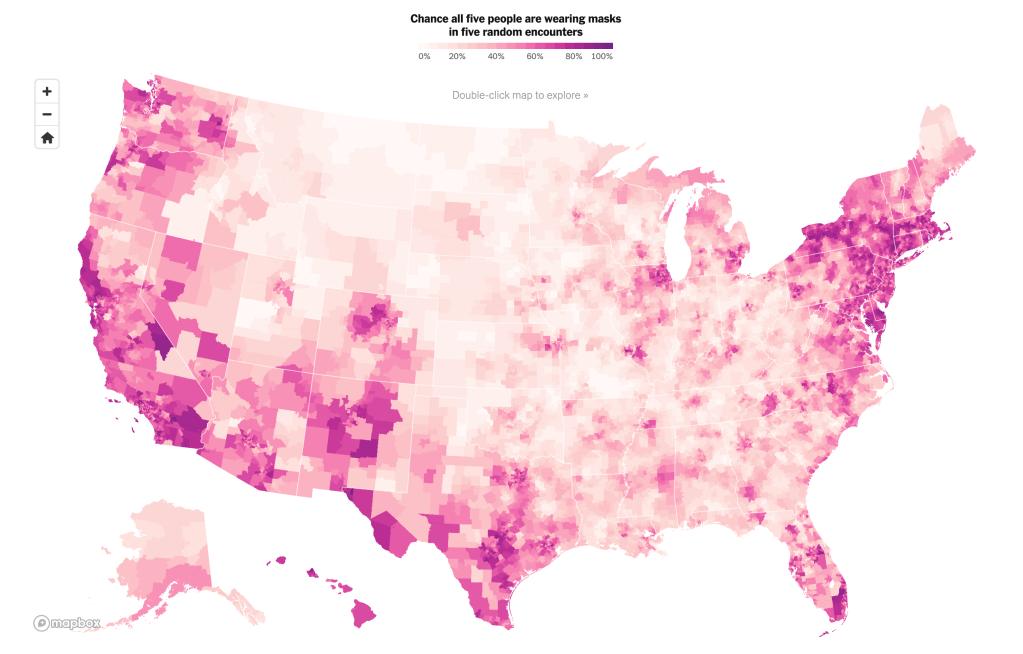
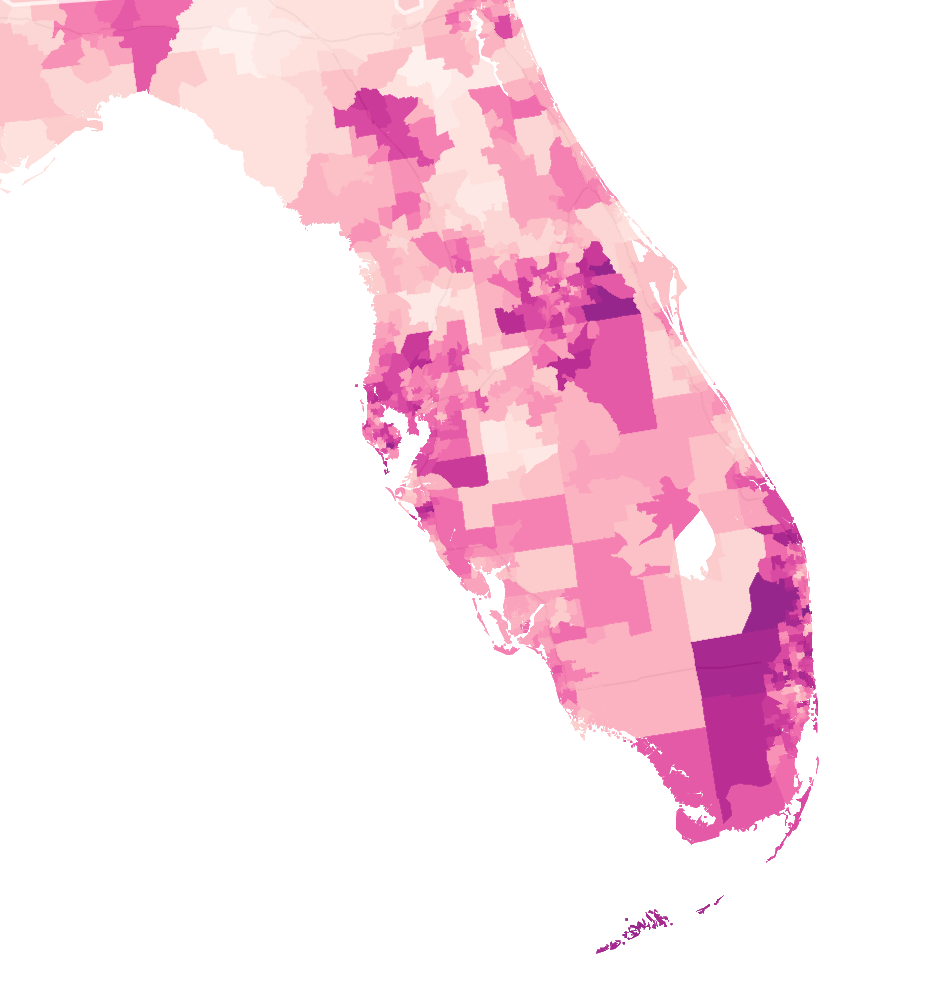
Interactive Data Visualization from NY Times July 17, 2020
The stark local divisions of adopting masks in public space won world-wide attention early in the pandemic. No masking regulations on beachfronts were a sort of albatross for the state governor DeSantis, famous for issuing a forceful Executive Order later in the month, resisting school boards trumpeted the absence of “well-grounded scientific justification” that mask-wearing reduced transmission and finding an absence of sufficient evidence masking could reduce community transmission in the state schools, had openly run against national opinion and allowed “all all parents have the right to make health care decisions for their minor children” affirmed patients’ “rights under Florida law” and vowed to protect all Floridians’ constitutional freedoms. By the time that the new CDC visualization dropped, anxiety was growing the rebound of COVID-19 both in Delta and omicron variants would kill the tourism industry for Christmas Vacation 2021, and DeSantis’ spokesperson must have been primed.
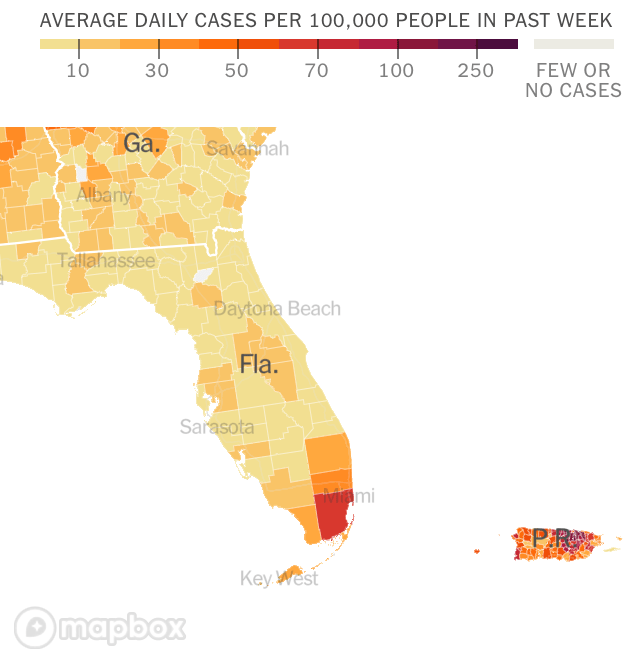
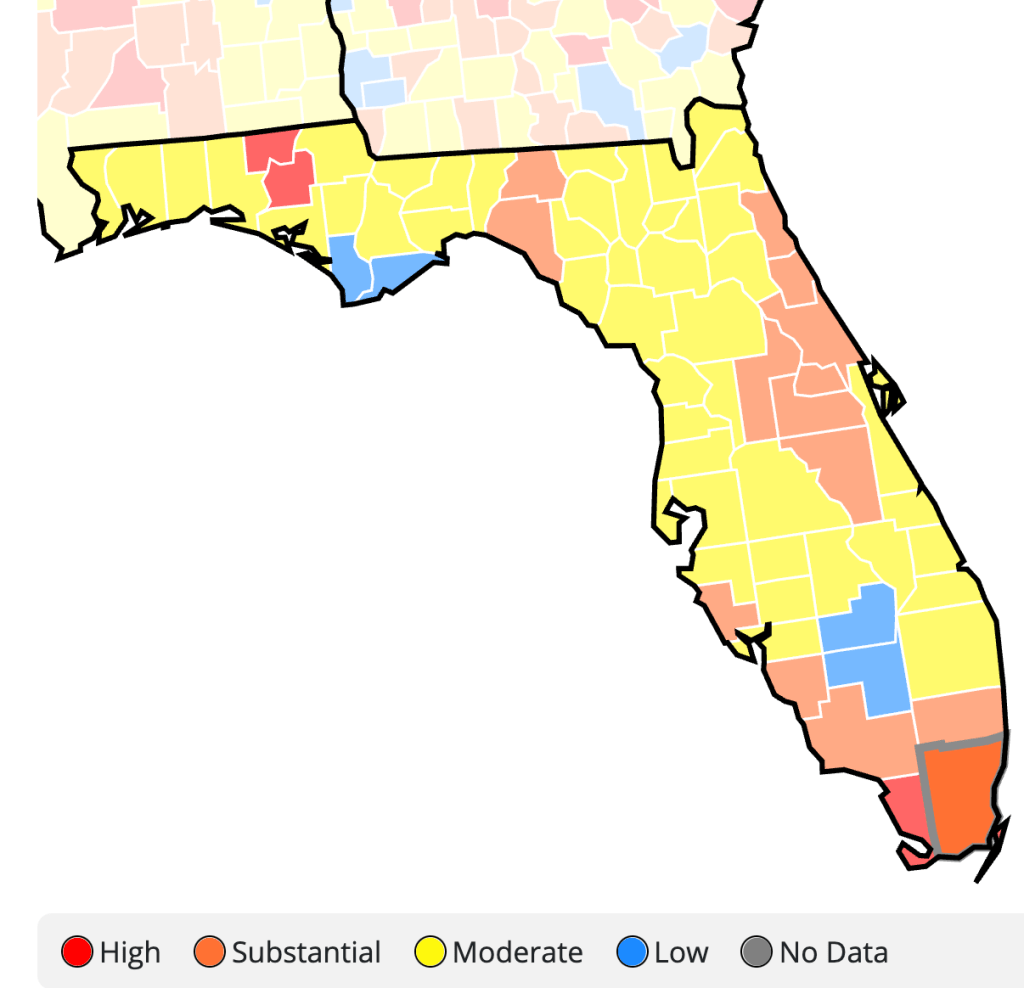
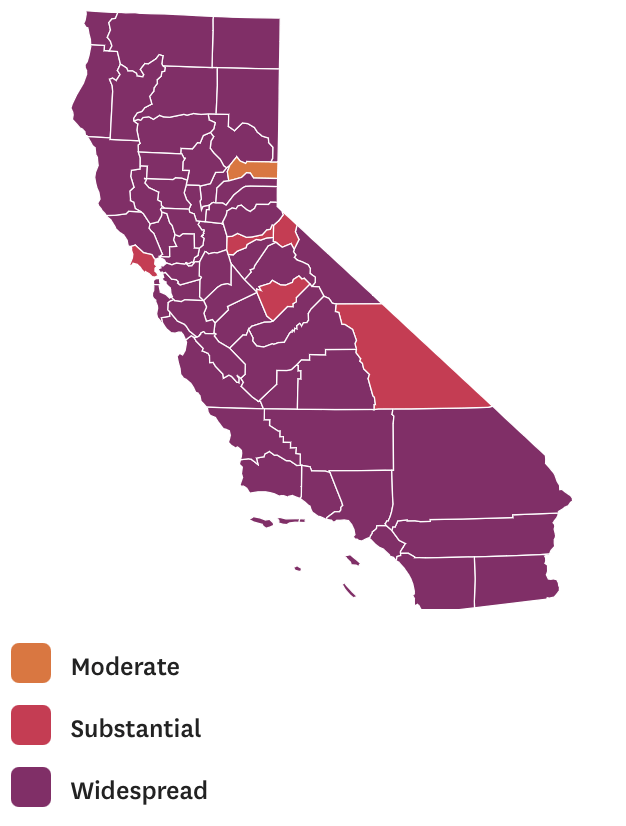
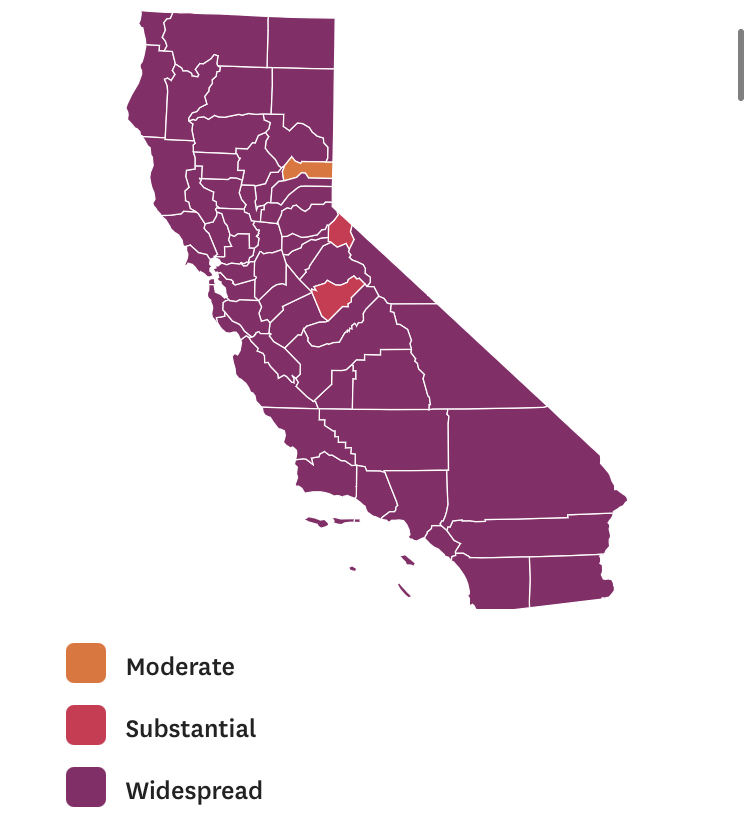
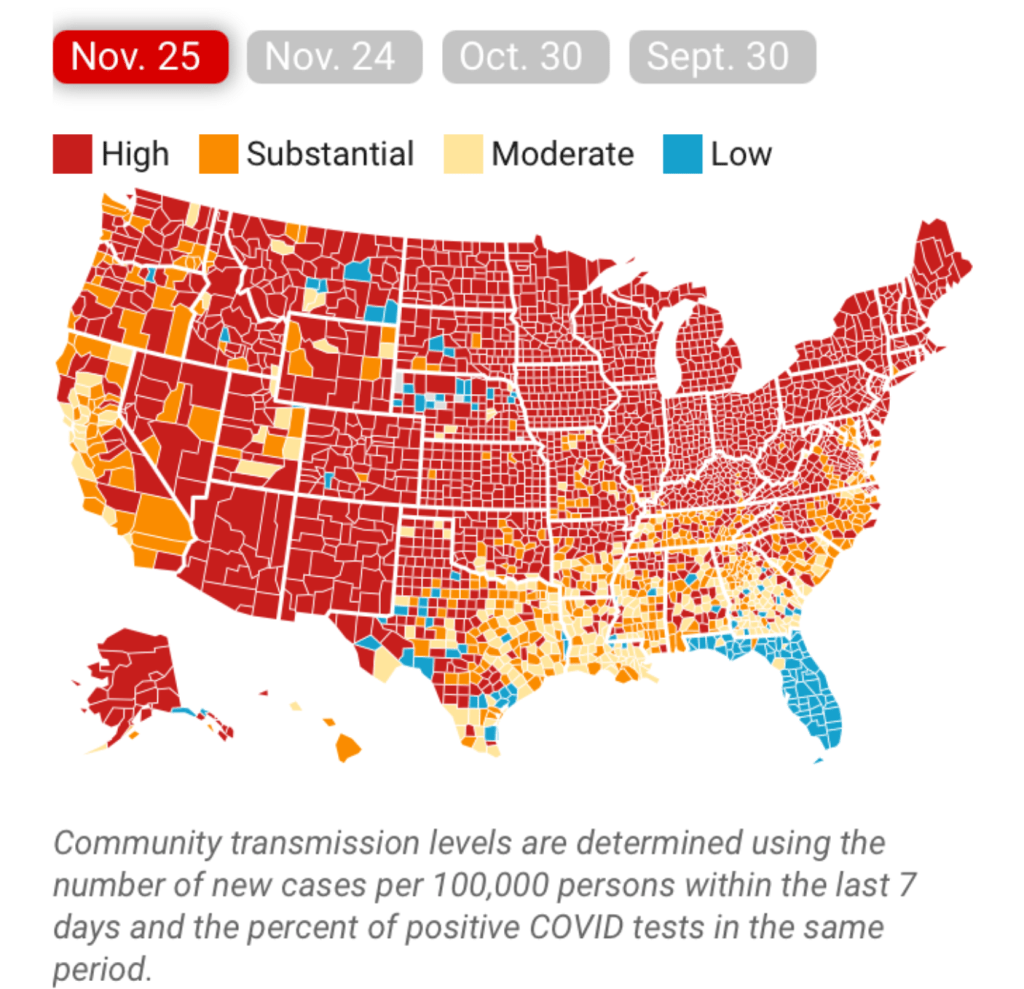
The flimsily persuasive nature of the cherry-picked data of the data vis can be handily spot checked on the CDC website itself, by stepping back just one day for a better view of the risk levels of putting caution aside and heading to the beach. For the lag of a few days of renewing data reminds us of how important the daily release of accurate data is, and how easily it can skew a national image of community transmission that seems to provide a “snapshot” of national levels. Florida’s rates of infection didn’t remain an island from the nation, so much as a lag in reporting failed to show comparable rates of infection to the rest of the nation. The differences were not so pronounced: indeed, the previous day–November 24–mapped the state as being a site of moderate and substantial transmission that could not have suddenly shifted in but one day, so much as the new visualization fit the “narrative” about DeSantis and COVID-19, more than the situation that Floridians experienced on the ground.
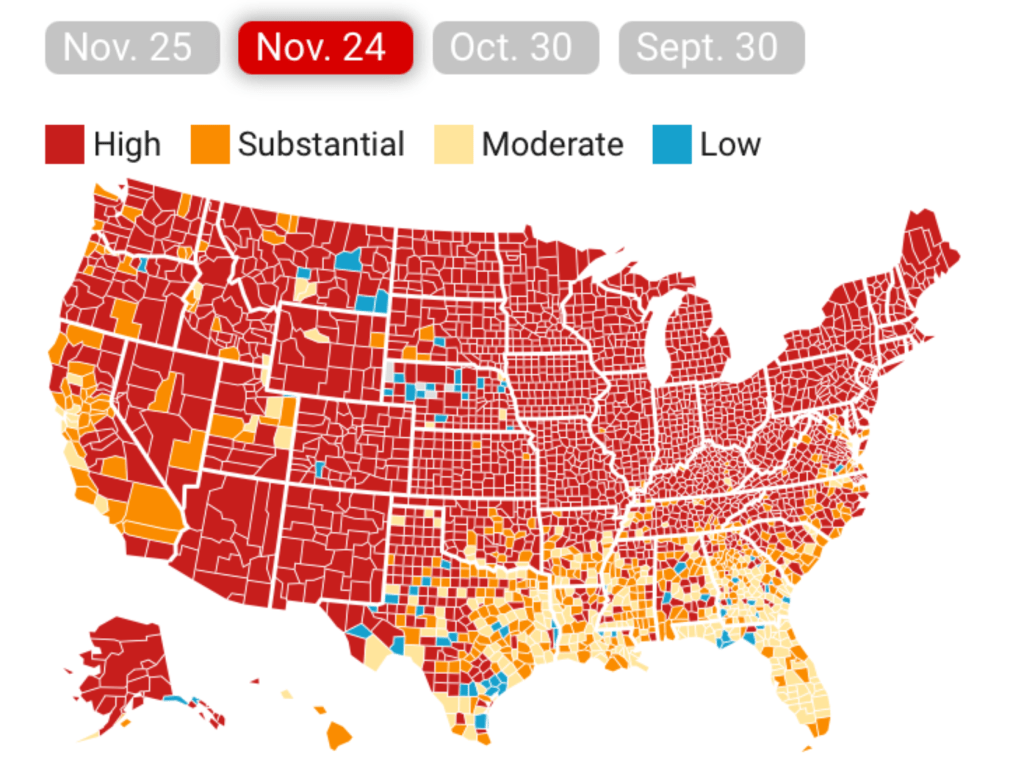
And flipping back just a few days previous, the stark divides of low rates of transmission and the substantial to high rates in other states offered little grounds for off the cuff collective diagnoses of the greater hardiness that exposure to COVID due no mask mandates offered a benefit to the state’s population, or might in fact be considered a viable public health policy: a month earlier, transmission seems roughly equivalent on the Florida or Texas coast, and relied on uniform assessment and tallies–but we may have reason to suspect Florida of undercounting to keep its numbers low.
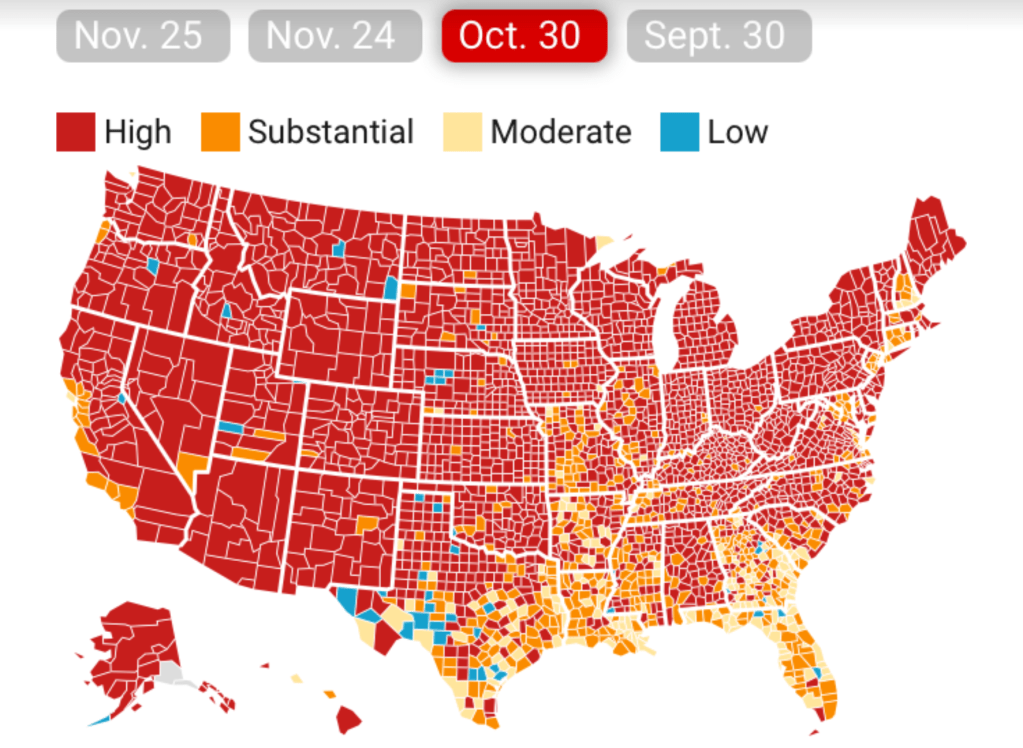
The lay of the land was basically not at all that clear-cut. One can only hope that few made travel plans after seeing that bright blue peninsula on social media: a better bet, it seems, would be Puerto Rico, if the mask-wearing mandate could be tolerated by visitors. In fact, the very areas that visitors might be hoping to travel–from Daytona Beach to Cocoa Beach, or the area around Miami and South Beach, down near the peninsula’s tip–suggested areas of substantial and even high risk, save for the area lying in the Everglades.
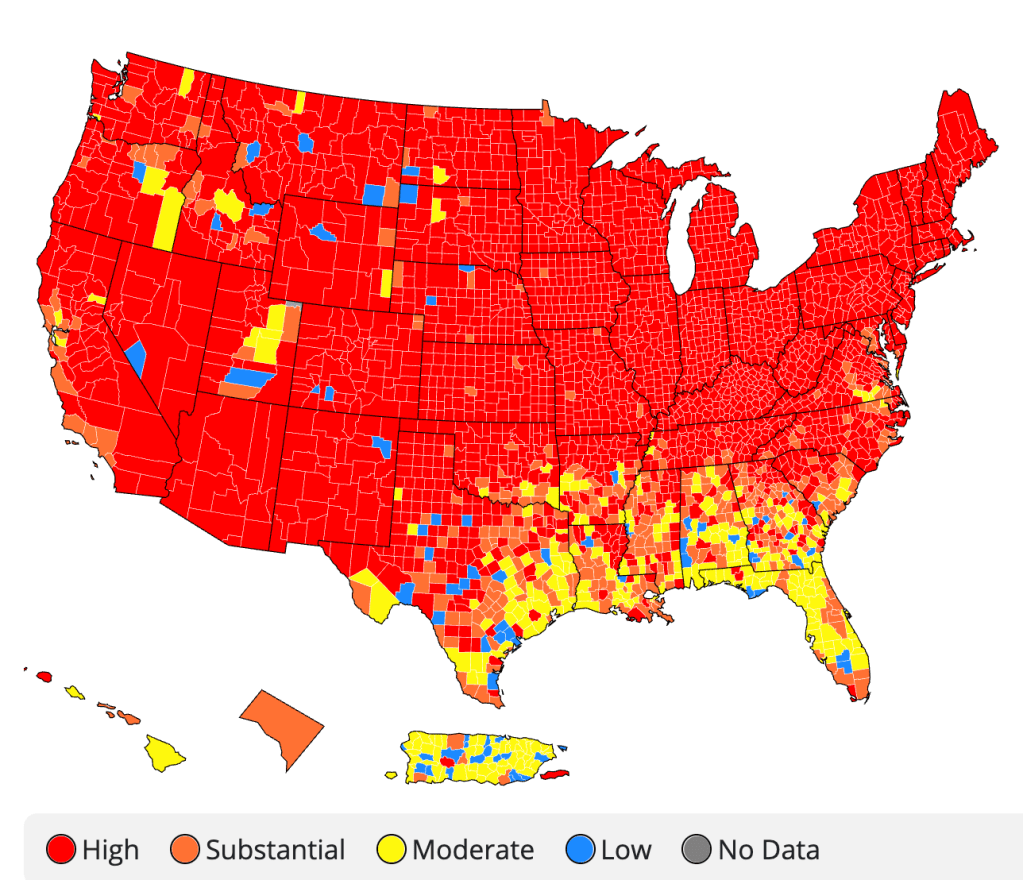
CDC Covid-19 Data Tracker by County
Indeed, a Moderate Risk seemed the fate of much of the state, if the tracker were looked at with regularly updated data sets. And this is relying on the numbers that the Department of Health provided–numbers that might be well scrutinized, given the complaints their former data guru had raised. All said and done, the “narrative” was not one of the power of a Governor to imagine his ability to purge COVID infections from the state, so much as a burst of virulence that demanded to be mapped and tracked in better detail.